1. What is a Special Right Triangle Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the longer leg, hypotenuse, perimeter, and area of special right triangles using the shorter leg and known side ratios.
Purpose: It simplifies calculations for common right triangle ratios, useful in geometry, construction, and engineering.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator operates in five modes based on the triangle type:
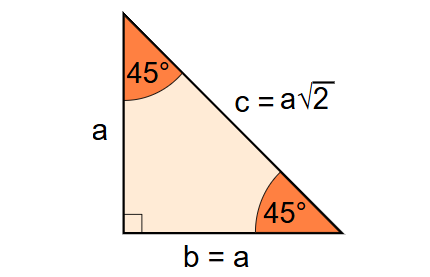
45°-45°-90° Triangle:
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = a \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = a \times \sqrt{2} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \)
30°-60°-90° Triangle:
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = a \times \sqrt{3} \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = 2 \times a \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \)
x-2x-√5x Triangle:
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = 2 \times a \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = a \times \sqrt{5} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \)
x-3x-√10x Triangle:
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = 3 \times a \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = a \times \sqrt{10} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \)
3x-4x-5x Triangle:
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = \frac{4}{3} \times a \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = \frac{5}{3} \times a \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \)
Unit Conversions:
- Input Dimensions: m, cm (1 m = 100 cm), mm (1 m = 1000 mm), in (1 m = 39.3701 in), ft (1 m = 3.28084 ft), yd (1 m = 1.09361 yd)
- Output Dimensions: m, cm, mm, in, ft, yd
- Output Area: m², cm² (1 m² = 10000 cm²), mm² (1 m² = 1000000 mm²), in² (1 m² = 1550.0031 in²), ft² (1 m² = 10.7639 ft²), yd² (1 m² = 1.19599 yd²)
Steps:
- Select the triangle type (45°-45°-90°, 30°-60°-90°, x-2x-√5x, x-3x-√10x, or 3x-4x-5x).
- View the corresponding triangle diagram for the selected type.
- Input the shorter leg \( a \) with its unit.
- Convert all dimensions to meters for calculation.
- Validate the input (e.g., positive values).
- Calculate the outputs based on the triangle's ratios, formatted to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Special Right Triangle Calculations
Calculating properties of special right triangles is crucial for:
- Geometry Education: Understanding common triangle ratios and their applications.
- Engineering Design: Simplifying structural calculations with known ratios.
- Construction: Ensuring accurate measurements for triangular components.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (45°-45°-90° Mode): For a triangle with \( a = 2 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.02 \, \text{m} \)
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = 0.02 \, \text{m} \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = 0.02 \times \sqrt{2} \approx 0.0283 \, \text{m} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 0.02 + 0.02 + 0.0283 \approx 0.0683 \, \text{m} \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.02 \times 0.02 = 0.0002 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Convert: \( b = 2 \, \text{cm} \), \( c \approx 2.83 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Perimeter} \approx 6.83 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Area} = 2 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Example 2 (30°-60°-90° Mode): For a triangle with \( a = 3 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.03 \, \text{m} \)
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = 0.03 \times \sqrt{3} \approx 0.05196 \, \text{m} \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = 2 \times 0.03 = 0.06 \, \text{m} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 0.03 + 0.05196 + 0.06 \approx 0.14196 \, \text{m} \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.03 \times 0.05196 \approx 0.0007794 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Convert: \( b \approx 5.196 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 6 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Perimeter} \approx 14.196 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Area} \approx 7.794 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Example 3 (x-2x-√5x Mode): For a triangle with \( a = 1 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.01 \, \text{m} \)
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = 2 \times 0.01 = 0.02 \, \text{m} \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = 0.01 \times \sqrt{5} \approx 0.02236 \, \text{m} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 0.01 + 0.02 + 0.02236 \approx 0.05236 \, \text{m} \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.01 \times 0.02 = 0.0001 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Convert: \( b = 2 \, \text{cm} \), \( c \approx 2.236 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Perimeter} \approx 5.236 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Area} = 1 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Example 4 (x-3x-√10x Mode): For a triangle with \( a = 1 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.01 \, \text{m} \)
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = 3 \times 0.01 = 0.03 \, \text{m} \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = 0.01 \times \sqrt{10} \approx 0.03162 \, \text{m} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 0.01 + 0.03 + 0.03162 \approx 0.07162 \, \text{m} \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.01 \times 0.03 = 0.00015 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Convert: \( b = 3 \, \text{cm} \), \( c \approx 3.162 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Perimeter} \approx 7.162 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Area} = 1.5 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Example 5 (3x-4x-5x Mode): For a triangle with \( a = 3 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.03 \, \text{m} \)
- Longer Leg \( b \): \( b = \frac{4}{3} \times 0.03 = 0.04 \, \text{m} \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = \frac{5}{3} \times 0.03 = 0.05 \, \text{m} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 0.03 + 0.04 + 0.05 = 0.12 \, \text{m} \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.03 \times 0.04 = 0.0006 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Convert: \( b = 4 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Perimeter} = 12 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Area} = 6 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are special right triangles?
A: Special right triangles are right triangles with specific angle or side ratios, such as 45°-45°-90°, 30°-60°-90°, or those with side ratios like 3:4:5, making calculations easier.
Q: Why are special right triangles important?
A: They simplify geometric calculations and are commonly used in math education, engineering, and construction due to their predictable ratios.
Special Right Triangle Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back