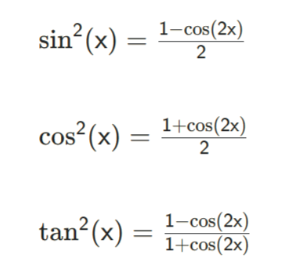1. What is a Power Reducing Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes trigonometric functions (\(\sin(x)\), \(\cos(x)\), \(\tan(x)\)) and their squared values (\(\sin^2(x)\), \(\cos^2(x)\), \(\tan^2(x)\)) either from an angle or from a given sine or cosine value.
Purpose: It helps in trigonometry to simplify expressions involving squared trigonometric functions, useful in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator operates in two modes:
An Angle Mode:
- \( \sin(x) \): \( \sin(x) = \sin(\alpha) \)
- \( \cos(x) \): \( \cos(x) = \cos(\alpha) \)
- \( \tan(x) \): \( \tan(x) = \frac{\sin(\alpha)}{\cos(\alpha)} \), undefined when \( \cos(\alpha) = 0 \)
- \( \sin^2(x) \): \( \sin^2(x) = (\sin(\alpha))^2 \)
- \( \cos^2(x) \): \( \cos^2(x) = (\cos(\alpha))^2 \)
- \( \tan^2(x) \): \( \tan^2(x) = (\tan(\alpha))^2 \), undefined when \( \cos(\alpha) = 0 \)
One of the Functions Mode:
- If given \( \sin(x) \):
- \( \cos(x) \): \( \cos(x) = \sqrt{1 - \sin^2(x)} \) (principal value)
- Angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \arcsin(\sin(x)) \)
- If given \( \cos(x) \):
- \( \sin(x) \): \( \sin(x) = \sqrt{1 - \cos^2(x)} \) (principal value)
- Angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \arccos(\cos(x)) \)
- \( \tan(x) \): \( \tan(x) = \frac{\sin(x)}{\cos(x)} \), undefined when \( \cos(x) = 0 \)
- \( \sin^2(x) \): \( \sin^2(x) = (\sin(x))^2 \)
- \( \cos^2(x) \): \( \cos^2(x) = (\cos(x))^2 \)
- \( \tan^2(x) \): \( \tan^2(x) = (\tan(x))^2 \), undefined when \( \cos(x) = 0 \)
Steps:
- Select the mode (An Angle or One of the Functions).
- View the corresponding diagram for the selected mode.
- For "One of the Functions" mode, choose the known function (\( \sin(x) \) or \( \cos(x) \)).
- Input the required values.
- Validate the inputs (e.g., angle between 0 and 360 degrees, \( \sin(x) \) or \( \cos(x) \) between -1 and 1).
- Calculate the outputs, formatted to 4 decimal places or in scientific notation for very small values.
3. Importance of Power Reducing Calculations
Power reducing calculations are crucial for:
- Trigonometry Education: Simplifying trigonometric identities and expressions.
- Physics: Analyzing wave equations and oscillations.
- Engineering: Solving problems involving trigonometric functions in design and analysis.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (An Angle Mode): For an angle \( \alpha = 30^\circ \):
- \( \sin(x) \): \( \sin(30^\circ) = 0.5000 \)
- \( \cos(x) \): \( \cos(30^\circ) \approx 0.8660 \)
- \( \tan(x) \): \( \tan(30^\circ) \approx 0.5774 \)
- \( \sin^2(x) \): \( (0.5000)^2 = 0.2500 \)
- \( \cos^2(x) \): \( (0.8660)^2 \approx 0.7500 \)
- \( \tan^2(x) \): \( (0.5774)^2 \approx 0.3333 \)
- Example 2 (One of the Functions Mode, \( \sin(x) \)): For \( \sin(x) = 0.5 \):
- \( \cos(x) \): \( \cos(x) = \sqrt{1 - (0.5)^2} \approx 0.8660 \)
- \( \tan(x) \): \( \tan(x) = \frac{0.5}{0.8660} \approx 0.5774 \)
- \( \sin^2(x) \): \( (0.5)^2 = 0.2500 \)
- \( \cos^2(x) \): \( (0.8660)^2 \approx 0.7500 \)
- \( \tan^2(x) \): \( (0.5774)^2 \approx 0.3333 \)
- Angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \arcsin(0.5) = 30^\circ \)
- Example 3 (One of the Functions Mode, \( \cos(x) \)): For \( \cos(x) = 1 \):
- \( \sin(x) \): \( \sin(x) = \sqrt{1 - (1)^2} = 0.0000 \)
- \( \tan(x) \): \( \tan(x) = \frac{0.0000}{1} = 0.0000 \)
- \( \sin^2(x) \): \( (0.0000)^2 = 0.0000 \)
- \( \cos^2(x) \): \( (1)^2 = 1.0000 \)
- \( \tan^2(x) \): \( (0.0000)^2 = 0.0000 \)
- Angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \arccos(1) = 0^\circ \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are power reducing formulas?
A: Power reducing formulas simplify squared trigonometric functions, such as \( \sin^2(x) \), \( \cos^2(x) \), and \( \tan^2(x) \), often derived from double-angle identities.
Q: Why are power reducing calculations important?
A: They are essential for simplifying trigonometric expressions in mathematics, physics, and engineering applications.
Power Reducing Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back