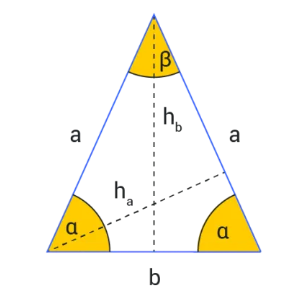
1. What is an Isosceles Triangle Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes properties of an isosceles triangle, including heights, angles, area, and perimeter, based on the lengths of the legs and base.
Purpose: It is used in geometry to determine various properties of an isosceles triangle, useful in education, design, and construction.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator takes the leg \( a \) and base \( b \) as inputs and computes the following:
- Height from base to vertex \( h_b \): \( h_b = \sqrt{a^2 - \left(\frac{b}{2}\right)^2} \)
- Height from leg to base corner \( h_a \): \( h_a = \frac{\frac{b}{2} \times h_b}{a} \)
- Base angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \cos^{-1}\left(\frac{\frac{b}{2}}{a}\right) \)
- Vertex angle \( \beta \): \( \beta = 180^\circ - 2\alpha \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{b \times h_b}{2} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2a + b \)
Unit Conversions:
- Input Dimensions: m, cm (1 m = 100 cm), mm (1 m = 1000 mm), in (1 m = 39.3701 in), ft (1 m = 3.28084 ft), yd (1 m = 1.09361 yd)
- Output Area: m², cm² (1 m² = 10000 cm²), mm² (1 m² = 1000000 mm²), in² (1 m² = 1550.0031 in²), ft² (1 m² = 10.7639 ft²), yd² (1 m² = 1.19599 yd²)
- Output Dimensions: m, cm, mm, in, ft, yd
Steps:
- Input the leg \( a \) and base \( b \) with their units.
- Convert all dimensions to meters for calculation.
- Validate the inputs (e.g., positive values, triangle inequality).
- Calculate the outputs using the formulas, formatted to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Isosceles Triangle Calculations
Calculating properties of an isosceles triangle is crucial for:
- Geometry Education: Understanding triangle properties and trigonometric relationships.
- Engineering Design: Analyzing symmetrical structures.
- Construction: Ensuring accurate measurements for triangular components.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For a triangle with \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 6 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.05 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 0.06 \, \text{m} \)
- Height \( h_b \): \( h_b = \sqrt{0.05^2 - \left(\frac{0.06}{2}\right)^2} = 0.04 \, \text{m} \)
- Height \( h_a \): \( h_a = \frac{\frac{0.06}{2} \times 0.04}{0.05} = 0.024 \, \text{m} \)
- Base angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \cos^{-1}\left(\frac{\frac{0.06}{2}}{0.05}\right) \approx 53.1301^\circ \)
- Vertex angle \( \beta \): \( \beta = 180 - 2 \times 53.1301 \approx 73.7398^\circ \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{0.06 \times 0.04}{2} = 0.0012 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times 0.05 + 0.06 = 0.16 \, \text{m} \)
- Convert: \( h_b = 4 \, \text{cm} \), \( h_a = 2.4 \, \text{cm} \), \( \text{Area} = 12 \, \text{cm}^2 \), \( \text{Perimeter} = 16 \, \text{cm} \)
- Example 2: For a triangle with \( a = 10 \, \text{in} \), \( b = 12 \, \text{in} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.254 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 0.3048 \, \text{m} \)
- Height \( h_b \): \( h_b = \sqrt{0.254^2 - \left(\frac{0.3048}{2}\right)^2} \approx 0.2032 \, \text{m} \)
- Height \( h_a \): \( h_a = \frac{\frac{0.3048}{2} \times 0.2032}{0.254} \approx 0.1219 \, \text{m} \)
- Base angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \cos^{-1}\left(\frac{\frac{0.3048}{2}}{0.254}\right) \approx 53.1301^\circ \)
- Vertex angle \( \beta \): \( \beta = 180 - 2 \times 53.1301 \approx 73.7398^\circ \)
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \frac{0.3048 \times 0.2032}{2} \approx 0.031 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times 0.254 + 0.3048 = 0.8128 \, \text{m} \)
- Convert: \( h_b = 8 \, \text{in} \), \( h_a = 4.8 \, \text{in} \), \( \text{Area} = 48 \, \text{in}^2 \), \( \text{Perimeter} = 32 \, \text{in} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is an isosceles triangle?
A: An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two sides of equal length, called the legs, and a third side called the base.
Q: Why is calculating isosceles triangle properties important?
A: It is essential for solving problems in geometry, engineering, and design involving symmetrical triangles.
Isosceles Triangle Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back