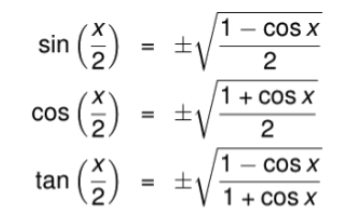1. What is the Half Angle Formula Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the half-angle identities for sine (\( \sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \)), cosine (\( \cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \)), and tangent (\( \tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \)) of a given angle \( x \), using the identities \( \sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos(x)}{2}} \), \( \cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 + \cos(x)}{2}} \), and \( \tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \frac{\sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)}{\cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)} \).
Purpose: It is used in trigonometry to simplify expressions, solve equations, and find trigonometric values of half angles, often in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following half-angle identities:
- \( \sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos(x)}{2}} \)
- \( \cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 + \cos(x)}{2}} \)
- \( \tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \frac{\sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)}{\cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)} \), or alternatively \( \tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \frac{1 - \cos(x)}{\sin(x)} \)
Note: The calculator assumes \( 0 \leq \frac{x}{2} \leq 90^\circ \) (or equivalent in other units) for simplicity, taking the positive square root for \( \sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \) and \( \cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \). For other ranges, the sign may need adjustment based on the quadrant.
Where:
- \( x \): The input angle in various units
Unit Conversions (Input Angle):
- Angle (\( x \)):
- Degrees (deg): Directly input in degrees
- Radians (rad): Directly input in radians
- Gradians (gon): \( \text{rad} = \text{gon} \times \frac{\pi}{200} \)
- Turns (tr): \( \text{rad} = \text{tr} \times 2\pi \)
- Minutes of Arc (arcmin): \( \text{rad} = \text{deg2rad}(\text{arcmin} / 60) \)
- Seconds of Arc (arcsec): \( \text{rad} = \text{deg2rad}(\text{arcsec} / 3600) \)
- Milliradians (mrad): \( \text{rad} = \text{mrad} / 1000 \)
- Microradians (urad): \( \text{rad} = \text{urad} / 1000000 \)
- π Radians (x π rad): \( \text{rad} = \text{x π rad} \times \pi \)
Steps:
- Enter the angle \( x \) and select its unit (e.g., deg, rad).
- Click "Calculate" to compute the half-angle values using the identities above.
- The results for \( \sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \), \( \cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \), and \( \tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \) are displayed with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Half Angle Formulas
Half-angle formulas are crucial for:
- Trigonometry: Simplifying expressions and solving trigonometric equations.
- Physics: Modeling periodic phenomena like waves and oscillations.
- Engineering: Analyzing signals, rotations, and structural mechanics.
4. Using the Calculator
Example:
Calculate the half-angle identities for \( x = 60^\circ \).
- Enter \( x = 60 \) and select the unit as "deg".
- Click "Calculate" to compute:
- \( \cos(60^\circ) = 0.5 \)
- \( \sin\left(\frac{60^\circ}{2}\right) = \sin(30^\circ) = \sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos(60^\circ)}{2}} = \sqrt{\frac{1 - 0.5}{2}} = \sqrt{0.25} = 0.5000 \)
- \( \cos\left(\frac{60^\circ}{2}\right) = \cos(30^\circ) = \sqrt{\frac{1 + \cos(60^\circ)}{2}} = \sqrt{\frac{1 + 0.5}{2}} = \sqrt{0.75} \approx 0.8660 \)
- \( \tan\left(\frac{60^\circ}{2}\right) = \tan(30^\circ) = \frac{\sin(30^\circ)}{\cos(30^\circ)} = \frac{0.5}{\sqrt{0.75}} \approx 0.5774 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are half-angle formulas?
A: Half-angle formulas express trigonometric functions of \( \frac{x}{2} \) in terms of functions of \( x \). For example, \( \sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos(x)}{2}} \), \( \cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 + \cos(x)}{2}} \), and \( \tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = \frac{\sin\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)}{\cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)} \).
Q: When is \( \tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) \) undefined?
A: The tangent of the half-angle is undefined when \( \cos\left(\frac{x}{2}\right) = 0 \), which occurs at angles like \( 90^\circ \), \( 270^\circ \), etc., after halving (e.g., \( x = 180^\circ \), \( 540^\circ \)).
Q: What are the different angle units?
A: Angles can be measured in various units:
- Degrees (deg): 360° in a full circle.
- Radians (rad): \( 2\pi \) in a full circle.
- Gradians (gon): 400 gon in a full circle.
- Turns (tr): 1 turn is a full circle.
- Minutes of Arc (arcmin): 60 arcmin per degree.
- Seconds of Arc (arcsec): 3600 arcsec per degree.
- Milliradians (mrad): 1000 mrad per radian.
- Microradians (urad): 1000000 urad per radian.
- π Radians (x π rad): Expressed as a multiple of π.
Half Angle Formula Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back