1. What is the Crescent Area Calculator?
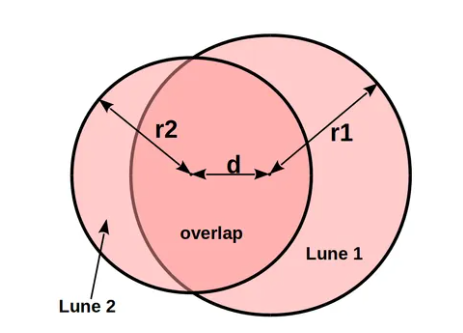
Definition: This calculator computes the areas of the two lunes (crescent-shaped regions) and the overlapping area formed by two intersecting circles with radii \( r_1 \) and \( r_2 \), and center distance \( d \).
Purpose: It assists in geometry problems involving intersecting circles, such as in optics, astronomy, or design applications.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
- Lune 1 Area: \( \text{lune}_1 = \frac{1}{2} \sqrt{(r_1 + r_2 + d)(r_2 + d - r_1)(d + r_1 - r_2)(r_1 + r_2 - d)} + r_1^2 \arccos\left(\frac{r_2^2 - r_1^2 - d^2}{2 \cdot r_1 \cdot d}\right) - r_2^2 \arccos\left(\frac{r_2^2 + d^2 - r_1^2}{2 \cdot r_2 \cdot d}\right) \)
- Overlap Area: \( \text{overlap area} = \pi r_1^2 - \text{lune}_1 \)
- Lune 2 Area: \( \text{lune}_2 = \pi r_2^2 - \text{overlap area} \)
Where:
- \( r_1 \): Radius of Circle 1 (mm, cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( r_2 \): Radius of Circle 2 (mm, cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( d \): Distance between circle centers (mm, cm, m, in, ft, or yd);
- \( \text{lune}_1 \): Area of Lune 1 (mm², cm², m², in², ft², or yd²);
- \( \text{lune}_2 \): Area of Lune 2 (mm², cm², m², in², ft², or yd²);
- \( \text{overlap area} \): Overlapping area of the two circles (mm², cm², m², in², ft², or yd²).
Steps:
- Enter the radii \( r_1 \), \( r_2 \), and the distance \( d \) along with their units (mm, cm, m, in, ft, or yd).
- Convert all inputs to SI units (meters).
- Calculate the area of Lune 1 using the formula above.
- Calculate the overlap area: \( \text{overlap area} = \pi r_1^2 - \text{lune}_1 \).
- Calculate the area of Lune 2: \( \text{lune}_2 = \pi r_2^2 - \text{overlap area} \).
- Convert results to the selected output units (mm², cm², m², in², ft², or yd²).
- Display results, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Crescent Area Calculations
Calculating the areas of lunes and overlaps is essential for:
Optics and Astronomy: Determines the visible area during phenomena like eclipses.
Design: Useful in creating patterns or shapes involving circular intersections.
Geometry Education: Helps in understanding advanced geometric concepts.
Engineering: Assists in calculating overlapping regions in mechanical or structural designs.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Metric Units): Calculate the crescent areas and overlap:
- Radius of Circle 1: \( r_1 = 5 \, \text{m} \);
- Radius of Circle 2: \( r_2 = 3 \, \text{m} \);
- Center Distance: \( d = 4 \, \text{m} \);
- Output Units: Square Meters (m²);
- Term 1: \( \frac{1}{2} \sqrt{(5+3+4)(3+4-5)(4+5-3)(5+3-4)} = \frac{1}{2} \sqrt{12 \cdot 2 \cdot 6 \cdot 4} = \frac{1}{2} \sqrt{576} = 12 \);
- Term 2: \( 5^2 \arccos\left(\frac{3^2 - 5^2 - 4^2}{2 \cdot 5 \cdot 4}\right) = 25 \arccos\left(\frac{9-25-16}{40}\right) = 25 \arccos(-0.8) \approx 25 \cdot 2.4981 \approx 62.4525 \);
- Term 3: \( 3^2 \arccos\left(\frac{3^2 + 4^2 - 5^2}{2 \cdot 3 \cdot 4}\right) = 9 \arccos\left(\frac{9+16-25}{24}\right) = 9 \arccos(0) = 9 \cdot \frac{\pi}{2} \approx 14.1372 \);
- Lune 1: \( 12 + 62.4525 - 14.1372 \approx 60.3153 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Circle 1 Area: \( \pi \cdot 5^2 \approx 78.5398 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Overlap: \( 78.5398 - 60.3153 \approx 18.2245 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Circle 2 Area: \( \pi \cdot 3^2 \approx 28.2743 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Lune 2: \( 28.2743 - 18.2245 \approx 10.0498 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Result: \( \text{Lune 1} = 60.3153 \, \text{m}^2 \), \( \text{Lune 2} = 10.0498 \, \text{m}^2 \), \( \text{Overlap} = 18.2245 \, \text{m}^2 \).
Example 2 (Mixed Units with yd²): Calculate the crescent areas and overlap:
- Radius of Circle 1: \( r_1 = 10 \, \text{ft} \);
- Radius of Circle 2: \( r_2 = 6 \, \text{ft} \);
- Center Distance: \( d = 8 \, \text{ft} \);
- Lune 1 Output Unit: Square Yards (yd²);
- Lune 2 Output Unit: Square Inches (in²);
- Overlap Output Unit: Square Feet (ft²);
- Convert to SI: \( r_1 = 10 \times 0.3048 = 3.048 \, \text{m} \), \( r_2 = 6 \times 0.3048 = 1.8288 \, \text{m} \), \( d = 8 \times 0.3048 = 2.4384 \, \text{m} \);
- Term 1: \( \frac{1}{2} \sqrt{(3.048+1.8288+2.4384)(1.8288+2.4384-3.048)(2.4384+3.048-1.8288)(3.048+1.8288-2.4384)} \approx 2.2318 \);
- Term 2: \( 3.048^2 \arccos\left(\frac{1.8288^2 - 3.048^2 - 2.4384^2}{2 \cdot 3.048 \cdot 2.4384}\right) \approx 23.1771 \);
- Term 3: \( 1.8288^2 \arccos\left(\frac{1.8288^2 + 2.4384^2 - 3.048^2}{2 \cdot 1.8288 \cdot 2.4384}\right) \approx 5.2629 \);
- Lune 1: \( 2.2318 + 23.1771 - 5.2629 \approx 20.1460 \, \text{m}^2 \approx 24.0947 \, \text{yd}^2 \);
- Circle 1 Area: \( \pi \cdot 3.048^2 \approx 29.1869 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Overlap: \( 29.1869 - 20.1460 \approx 9.0409 \, \text{m}^2 \approx 97.3162 \, \text{ft}^2 \);
- Circle 2 Area: \( \pi \cdot 1.8288^2 \approx 10.5071 \, \text{m}^2 \);
- Lune 2: \( 10.5071 - 9.0409 \approx 1.4662 \, \text{m}^2 \approx 2272.6100 \, \text{in}^2 \);
- Result: \( \text{Lune 1} = 24.0947 \, \text{yd}^2 \), \( \text{Lune 2} = 2272.6100 \, \text{in}^2 \), \( \text{Overlap} = 97.3162 \, \text{ft}^2 \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What happens if the circles do not overlap?
A: If the distance \( d \) is greater than \( r_1 + r_2 \), the circles do not overlap, and the calculator will display an error.
Q: What if one circle is completely inside the other?
A: If \( d \leq |r_1 - r_2| \), one circle is inside the other, and no crescent is formed; the calculator will display an error.
Q: Can I use different units for each input and output?
A: Yes, the calculator allows independent unit selection for \( r_1 \), \( r_2 \), \( d \), and all output areas.
Crescent Area Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back