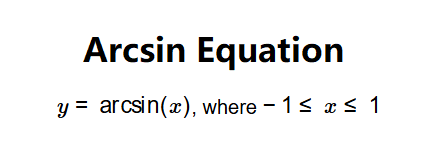1. What is the Arcsin (Inverse Sine) Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the inverse sine (\( y = \arcsin(x) \)) of a given value \( x \), where \( -1 \leq x \leq 1 \). The result is the angle \( y \) whose sine is \( x \).
Purpose: It is used in mathematics, physics, and engineering to find angles based on sine values, often in problems involving trigonometry, geometry, or wave analysis.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the inverse sine function:
- \( y = \arcsin(x) \), where \( -1 \leq x \leq 1 \)
Where:
- \( x \): The input value (sine of the angle)
- \( y \): The angle in various units
Unit Conversions:
- Angle (\( y \)):
- Radians (rad): The default output of the inverse sine function
- Degrees (deg): \( \text{deg} = \text{rad} \times \frac{180}{\pi} \)
- Gradians (gon): \( \text{gon} = \text{rad} \times \frac{200}{\pi} \)
- Turns (tr): \( \text{tr} = \text{rad} \times \frac{1}{2\pi} \)
- Minutes of Arc (arcmin): \( \text{arcmin} = \text{rad} \times \frac{180}{\pi} \times 60 \)
- Seconds of Arc (arcsec): \( \text{arcsec} = \text{rad} \times \frac{180}{\pi} \times 3600 \)
- Milliradians (mrad): \( \text{mrad} = \text{rad} \times 1000 \)
- Microradians (urad): \( \text{urad} = \text{rad} \times 1000000 \)
- π Radians (x π rad): \( \text{x π rad} = \text{rad} \times \frac{1}{\pi} \)
Steps:
- Enter the value \( x \) (between -1 and 1).
- Click "Calculate" to compute \( y = \arcsin(x) \).
- Select the desired unit (e.g., deg, rad, gon) for the result.
- The result is displayed with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Arcsin Calculation
Calculating the inverse sine is crucial for:
- Trigonometry: Finding angles in right triangles or other geometric shapes.
- Physics: Analyzing angles in wave mechanics, optics, or projectile motion.
- Engineering: Solving problems in signal processing, robotics, or structural analysis.
4. Using the Calculator
Example:
Calculate the inverse sine of \( x = 0.5 \).
- Enter \( x = 0.5 \) in the input field.
- Click "Calculate" to compute:
- In radians: \( y = \arcsin(0.5) = \frac{\pi}{6} \approx 0.5236 \, \text{rad} \)
- In degrees: \( y = 0.5236 \times \frac{180}{\pi} = 30.0000 \, \text{deg} \)
- In gradians: \( y = 0.5236 \times \frac{200}{\pi} \approx 33.3333 \, \text{gon} \)
- In turns: \( y = 0.5236 \times \frac{1}{2\pi} \approx 0.0833 \, \text{tr} \)
- In minutes of arc: \( y = 30 \times 60 = 1800.0000 \, \text{arcmin} \)
- In seconds of arc: \( y = 30 \times 3600 = 108000.0000 \, \text{arcsec} \)
- In milliradians: \( y = 0.5236 \times 1000 = 523.5988 \, \text{mrad} \)
- In microradians: \( y = 0.5236 \times 1000000 = 523598.7756 \, \text{urad} \)
- In π radians: \( y = 0.5236 \times \frac{1}{\pi} \approx 0.1667 \, \text{x π rad} \)
- Select the unit to view the result in the desired format.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the inverse sine (arcsin)?
A: The inverse sine (\( \arcsin(x) \)) is the angle \( y \) such that \( \sin(y) = x \), where \( -1 \leq x \leq 1 \). The result is typically between \( -\frac{\pi}{2} \) and \( \frac{\pi}{2} \) radians (or -90° to 90°).
Q: Why must the input be between -1 and 1?
A: The sine function only produces values between -1 and 1. Therefore, the inverse sine is only defined for inputs in this range.
Q: What are the different angle units?
A: Angles can be measured in various units:
- Degrees (deg): 360° in a full circle.
- Radians (rad): \( 2\pi \) in a full circle.
- Gradians (gon): 400 gon in a full circle.
- Turns (tr): 1 turn is a full circle.
- Minutes of Arc (arcmin): 60 arcmin per degree.
- Seconds of Arc (arcsec): 3600 arcsec per degree.
- Milliradians (mrad): 1000 mrad per radian.
- Microradians (urad): 1000000 urad per radian.
- π Radians (x π rad): Expressed as a multiple of π.
Arcsin (Inverse Sine) Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back