LPM to PSI Conversion Relationship
The pressure loss (PSI) due to flow rate (LPM) in a pipe can be calculated using the Hazen-Williams formula, adjusted for LPM. The formula is as follows:
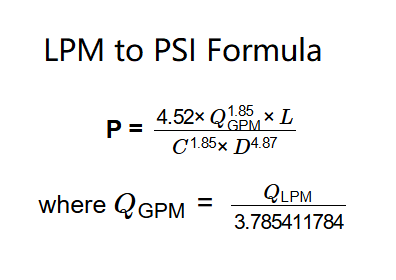
P = \( \frac{4.52 \times Q_{\text{GPM}}^{1.85} \times L}{C^{1.85} \times D^{4.87}} \), where \( Q_{\text{GPM}} = \frac{Q_{\text{LPM}}}{3.785411784} \)
Where:
- P = Pressure loss (PSI)
- QLPM = Flow rate (Liters per Minute, LPM)
- QGPM = Flow rate (Gallons per Minute, GPM), calculated as QGPM = QLPM / 3.785411784
- L = Pipe length (feet)
- C = Hazen-Williams coefficient (depends on pipe material)
- D = Pipe diameter (inches)
This formula helps determine the pressure loss in a pipe system based on the flow rate, pipe dimensions, and material properties.
Input Parameters:
- Flow Rate: Volume of fluid per unit time (e.g., LPM, LPH, L/s, m³/h, GPM).
- Pipe Length: Length of the pipe (m or ft).
- Pipe Diameter: Inner diameter of the pipe (mm or in).
- Hazen-Williams Coefficient (C): Depends on pipe material:
- Asbestos-cement: 140
- Cast iron new: 130
- Cast iron 10 years: 113
- Cast iron 20 years: 100
- Cement-Mortar Lined Ductile Iron: 140
- Concrete: 140
- Copper: 140
- Steel: 120
- Galvanized iron: 120
- Polyethylene: 140
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): 150
- Fibre-reinforced plastic (FRP): 150
- Custom: User-defined (50-200)
Practical Applications
This calculator is useful in:
- Plumbing: Estimate pressure drop in water supply lines.
- Irrigation: Calculate pressure loss for sprinkler systems.
- Engineering: Design piping systems with acceptable pressure losses.
Example Calculation
Let’s calculate the pressure loss for a flow rate of 0.01 LPM, a pipe length of 10 meters, a pipe diameter of 100 mm, and a PVC pipe (C = 150).
Step 1: Convert Flow Rate to GPM
Convert 0.01 LPM to GPM using the conversion factor 1 LPM ≈ 0.264172 GPM:
\[ Q_{\text{GPM}} = \frac{0.01}{3.785411784} \approx 0.002641 \, \text{GPM} \]
Step 2: Convert Pipe Length to Feet
Convert 10 meters to feet using 1 m = 3.28084 ft:
\[ L = 10 \times 3.28084 = 32.8084 \, \text{ft} \]
Step 3: Convert Pipe Diameter to Inches
Convert 100 mm to inches using 1 mm = 0.0393701 in:
\[ D = \frac{100}{25.4} \approx 3.937 \, \text{in} \]
Step 4: Calculate Pressure Loss (PSI)
Apply the Hazen-Williams formula:
\[ P = \frac{4.52 \times Q_{\text{GPM}}^{1.85} \times L}{C^{1.85} \times D^{4.87}} \]
Substitute the values (\( Q_{\text{GPM}} = 0.002641 \), \( L = 32.8084 \), \( C = 150 \), \( D = 3.937 \)):
\[ P = \frac{4.52 \times 0.002641^{1.85} \times 32.8084}{150^{1.85} \times 3.937^{4.87}} \approx 0.000038 \, \text{PSI} \]
Displayed as: 3.80E-5 PSI (using scientific notation for small values).
Step 5: Convert to Other Units
Convert PSI to bar (1 PSI = 0.0689475729 bar) and kPa (1 PSI = 6.89475729 kPa):
- Bar: \( 0.000038 \times 0.0689475729 \approx 0.00000262 \, \text{bar} \), displayed as 2.62E-6 bar
- kPa: \( 0.000038 \times 6.89475729 \approx 0.000262 \, \text{kPa} \), displayed as 2.62E-4 kPa
Conversion Constants
Key conversion factors:
- 1 Liter = 0.264172 Gallons
- 1 m = 3.28084 ft
- 1 mm = 0.0393701 in
- 1 PSI = 0.0689475729 bar = 6.89475729 kPa
 Home
Home
 Back
Back