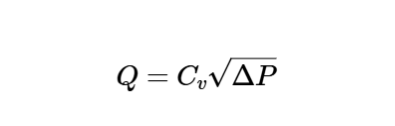1. What is a Valve Flow Rate Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the volumetric flow rate (\( Q \)) through a valve, using the valve coefficient and pressure drop across the valve.
Purpose: It is used in fluid dynamics and HVAC design to determine the flow rate through valves, aiding in valve selection and system performance optimization.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for volumetric flow rate:
Volumetric Flow Rate:
\[
Q = C_v \sqrt{\Delta P}
\]
Where:
- \( Q \): Volumetric flow rate (gpm, m³/s)
- \( C_v \): Valve coefficient (gpm/(psi)^0.5, m³/s/(Pa)^0.5)
- \( \Delta P \): Pressure drop across the valve (psi, Pa)
Unit Conversions:
- Valve Coefficient (\( C_v \)): gpm/(psi)^0.5, m³/s/(Pa)^0.5 (1 m³/s/(Pa)^0.5 = 1.57488e6 gpm/(psi)^0.5)
- Pressure Drop (\( \Delta P \)): psi, Pa (1 Pa = 0.000145038 psi)
- Volumetric Flow Rate (\( Q \)): gpm, m³/s (1 gpm = 6.30902e-5 m³/s)
Steps:
- Enter the valve coefficient (\( C_v \)) and pressure drop (\( \Delta P \)), and select their units.
- Convert \( C_v \) and \( \Delta P \) to gpm/(psi)^0.5 and psi, respectively.
- Calculate the volumetric flow rate using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (gpm or m³/s).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Valve Flow Rate Calculation
Calculating the valve flow rate is crucial for:
- Valve Selection: Ensures the valve can handle the required flow rate for the system.
- System Design: Optimizes pressure drop and flow conditions in piping systems.
- System Performance: Maintains proper fluid flow for industrial, HVAC, or plumbing applications.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( C_v = 10 \, \text{gpm/(psi)^0.5} \), \( \Delta P = 4 \, \text{psi} \), volumetric flow rate in gpm:
- \( Q = 10 \times \sqrt{4} = 10 \times 2 = 20 \)
- Since 20 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 20.00000 \)
- Example 2: For \( C_v = 0.00001 \, \text{m³/s/(Pa)^0.5} \), \( \Delta P = 10000 \, \text{Pa} \), volumetric flow rate in m³/s:
- Convert: \( C_v = 0.00001 \times 1.57488e6 \approx 15.7488 \, \text{gpm/(psi)^0.5} \)
- \( \Delta P = 10000 \times 0.000145038 \approx 1.45038 \, \text{psi} \)
- \( Q = 15.7488 \times \sqrt{1.45038} \approx 15.7488 \times 1.20431 \approx 18.966 \, \text{gpm} \)
- Convert to m³/s: \( 18.966 \times 6.30902e-5 \approx 0.001196 \)
- Since 0.001196 < 0.00001, display in scientific notation: \( 1.19600 \times 10^{-3} \)
- Example 3: For \( C_v = 5 \, \text{gpm/(psi)^0.5} \), \( \Delta P = 9 \, \text{psi} \), volumetric flow rate in gpm:
- \( Q = 5 \times \sqrt{9} = 5 \times 3 = 15 \)
- Since 15 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 15.00000 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does valve flow rate represent?
A: Valve flow rate (\( Q \)) quantifies the volume of fluid passing through a valve per unit time, critical for ensuring proper system operation.
Q: How can I determine the input parameters?
A: The valve coefficient (\( C_v \)) is provided by the valve manufacturer or determined experimentally. Pressure drop (\( \Delta P \)) is measured across the valve or calculated based on system conditions.
Q: Why is valve flow rate important in pipe system design?
A: It ensures valves are appropriately sized to achieve the desired flow rate, optimizing system performance and efficiency.
Valve Flow Rate Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back