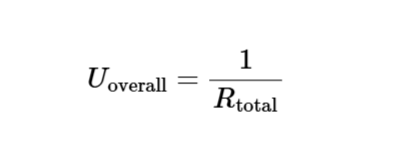1. What is an Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient (U-Factor) Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the overall heat transfer coefficient (\( U_{\text{overall}} \)) as the reciprocal of the total thermal resistance, used to quantify heat transfer through composite walls or structures.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems, building design, and thermal engineering to assess heat transfer rates through multi-layered materials, aiding in energy-efficient design and insulation selection.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for the U-factor:
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient:
\[
U_{\text{overall}} = \frac{1}{R_{\text{total}}}
\]
Where:
- \( U_{\text{overall}} \): Overall heat transfer coefficient (Btu/hr-ft²-°F, W/m²-K)
- \( R_{\text{total}} \): Total thermal resistance (hr-ft²-°F/Btu, m²-K/W)
Unit Conversions:
- Total Thermal Resistance (\( R_{\text{total}} \)): hr-ft²-°F/Btu, m²-K/W (1 m²-K/W = 5.678263 hr-ft²-°F/Btu)
- U-Factor (\( U_{\text{overall}} \)): Btu/hr-ft²-°F, W/m²-K (1 Btu/hr-ft²-°F = 5.678263 W/m²-K)
Steps:
- Enter the total thermal resistance (\( R_{\text{total}} \)) and select its unit.
- Convert total thermal resistance to hr-ft²-°F/Btu.
- Calculate the U-factor using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (Btu/hr-ft²-°F or W/m²-K).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of U-Factor Calculation
Calculating the U-factor is crucial for:
- HVAC Design: Determines heat transfer rates through composite walls, aiding in the sizing of heating and cooling equipment.
- Energy Efficiency: Helps evaluate the thermal performance of building envelopes, guiding insulation improvements to reduce energy consumption.
- Thermal Comfort: Ensures indoor temperatures remain comfortable by minimizing unwanted heat loss or gain.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( R_{\text{total}} = 20.7 \, \text{hr-ft²-°F/Btu} \), U-factor in Btu/hr-ft²-°F:
- \( U_{\text{overall}} = \frac{1}{20.7} \approx 0.048309 \)
- Since 0.048309 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.04831 \)
- Example 2: For \( R_{\text{total}} = 3.5 \, \text{m²-K/W} \), U-factor in W/m²-K:
- Convert: \( R_{\text{total}} = 3.5 \times 5.678263 = 19.8739205 \, \text{hr-ft²-°F/Btu} \)
- \( U_{\text{overall}} = \frac{1}{19.8739205} \approx 0.050307 \, \text{Btu/hr-ft²-°F} \)
- Convert to W/m²-K: \( 0.050307 \times 5.678263 \approx 0.285714 \)
- Since 0.285714 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.28571 \)
- Example 3: For \( R_{\text{total}} = 10 \, \text{hr-ft²-°F/Btu} \), U-factor in Btu/hr-ft²-°F:
- \( U_{\text{overall}} = \frac{1}{10} = 0.1 \)
- Since 0.1 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.10000 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does the U-factor represent?
A: The U-factor (\( U_{\text{overall}} \)) measures the rate of heat transfer through a material or assembly per unit area and temperature difference. A lower U-factor indicates better insulation.
Q: Why is the U-factor important in building design?
A: It quantifies the thermal performance of walls, windows, and roofs, helping designers select materials to minimize heat loss or gain for energy efficiency and comfort.
Q: How can I determine the total thermal resistance?
A: Total thermal resistance (\( R_{\text{total}} \)) is the sum of individual resistances of material layers, including conduction, convection, and radiation resistances, obtained from material properties or calculations.
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient (U-Factor) Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back