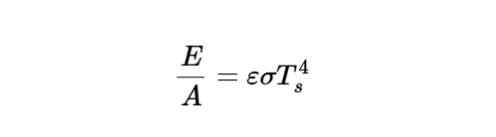1. What is a Surface Emissive Power Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the emissive power per unit area (\( \frac{E}{A} \)) of a real surface using the Stefan-Boltzmann law, adjusted by the surface's emissivity.
Purpose: It is used in thermal engineering, HVAC systems, and radiative heat transfer analysis to quantify the rate of thermal radiation emitted by a surface, aiding in the design of radiative cooling systems and thermal shields.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for emissive power per unit area:
Surface Emissive Power:
\[
\frac{E}{A} = \varepsilon \sigma T_s^4
\]
Where:
- \( \frac{E}{A} \): Emissive power per unit area (Btu/hr-ft², W/m²)
- \( \varepsilon \): Emissivity (dimensionless, 0 to 1)
- \( \sigma \): Stefan-Boltzmann constant (\( 0.1714 \times 10^{-8} \text{ Btu/hr-ft²-°R}^4 \))
- \( T_s \): Surface temperature (°R, °F, °C, or K)
Unit Conversions:
- Surface Temperature (\( T_s \)):
- °F to °R: °R = °F + 460
- °C to °R: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32, then °R = °F + 460
- K to °R: °C = K - 273.15, then °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32, then °R = °F + 460
- Emissive Power per Unit Area (\( \frac{E}{A} \)): Btu/hr-ft², W/m² (1 Btu/hr-ft² = 3.154591 W/m²)
Steps:
- Enter the emissivity (\( \varepsilon \)) and surface temperature (\( T_s \)), and select the temperature unit.
- Convert the surface temperature to °R.
- Calculate the emissive power per unit area using the formula, with \( \sigma = 0.1714 \times 10^{-8} \text{ Btu/hr-ft²-°R}^4 \).
- Convert the result to the selected unit (Btu/hr-ft² or W/m²).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Surface Emissive Power Calculation
Calculating the emissive power per unit area is crucial for:
- Thermal Engineering: Quantifies the radiative heat emitted by surfaces, aiding in the design of thermal management systems.
- HVAC Systems: Helps evaluate radiative heat losses or gains in buildings, improving energy efficiency.
- Radiative Cooling: Assists in designing systems that use radiative heat transfer to cool structures or equipment.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( \varepsilon = 0.80 \), \( T_s = 400 \, \text{°F} \), emissive power in Btu/hr-ft²:
- Convert: \( T_s = 400 + 460 = 860 \, \text{°R} \)
- \( \frac{E}{A} = 0.80 \times 0.1714 \times 10^{-8} \times 860^4 \)
- \( 860^4 \approx 5.4617 \times 10^{11} \)
- \( \frac{E}{A} \approx 0.80 \times 0.1714 \times 10^{-8} \times 5.4617 \times 10^{11} \approx 749.199 \)
- Since 749.199 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 749.19900 \)
- Example 2: For \( \varepsilon = 0.95 \), \( T_s = 500 \, \text{°C} \), emissive power in W/m²:
- Convert: \( T_s = (500 \times 9/5) + 32 + 460 = 900 + 32 + 460 = 1392 \, \text{°R} \)
- \( \frac{E}{A} = 0.95 \times 0.1714 \times 10^{-8} \times 1392^4 \)
- \( 1392^4 \approx 3.7527 \times 10^{12} \)
- \( \frac{E}{A} \approx 0.95 \times 0.1714 \times 10^{-8} \times 3.7527 \times 10^{12} \approx 6109.345 \, \text{Btu/hr-ft²} \)
- Convert to W/m²: \( 6109.345 \times 3.154591 \approx 19271.517 \)
- Since 19271.517 > 10000, display in scientific notation: \( 1.92715 \times 10^4 \)
- Example 3: For \( \varepsilon = 0.50 \), \( T_s = 773.15 \, \text{K} \), emissive power in Btu/hr-ft²:
- Convert: \( T_s = (773.15 - 273.15) = 500 \, \text{°C} \), then \( (500 \times 9/5) + 32 + 460 = 1392 \, \text{°R} \)
- \( \frac{E}{A} = 0.50 \times 0.1714 \times 10^{-8} \times 1392^4 \)
- \( \frac{E}{A} \approx 0.50 \times 0.1714 \times 10^{-8} \times 3.7527 \times 10^{12} \approx 3215.445 \)
- Since 3215.445 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 3215.44500 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does emissive power per unit area represent?
A: Emissive power per unit area (\( \frac{E}{A} \)) quantifies the rate of thermal radiation emitted by a surface per unit area, based on its temperature and emissivity.
Q: Why is emissivity important in this calculation?
A: Emissivity (\( \varepsilon \)) indicates how efficiently a surface emits radiation compared to a perfect blackbody. Values range from 0 to 1, with real surfaces having \( \varepsilon < 1 \).
Q: How can I determine the emissivity of a surface?
A: Emissivity can be found in material property tables, manufacturer specifications, or through experimental measurements for materials like metals, paints, or coatings.
Surface Emissive Power Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back