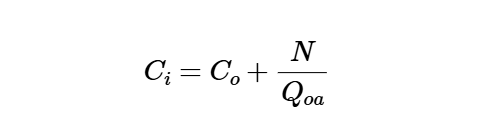1. What is a Steady-State Indoor Pollutant Concentration Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the steady-state indoor concentration of a pollutant (\( C_i \)) in a space, considering the outdoor concentration, pollutant generation rate, and ventilation rate, assuming thorough mixing and stable conditions.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to assess indoor air quality by predicting pollutant levels, aiding in the design of ventilation systems to maintain safe and healthy indoor environments.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for steady-state indoor pollutant concentration:
Steady-State Indoor Concentration:
\[
C_i = C_o + \frac{N}{Q_{oa}}
\]
Where:
- \( C_i \): Steady-state indoor concentration (µg/ft³ or ppm)
- \( C_o \): Steady outdoor concentration (µg/ft³ or ppm)
- \( N \): Total indoor pollutant generation rate (µg/min or ppm·cfm)
- \( Q_{oa} \): Ventilation rate (cfm, m³/s, L/s)
Unit Conversions:
- Ventilation Rate (\( Q_{oa} \)): cfm, m³/s (1 m³/s = 2118.88 cfm), L/s (1 L/s = 2.11888 cfm)
- Concentration Units: µg/ft³ (with \( N \) in µg/min) or ppm (with \( N \) in ppm·cfm)
Steps:
- Select the concentration unit (µg/ft³ or ppm) to ensure consistency.
- Enter the steady outdoor concentration (\( C_o \)), total indoor pollutant generation rate (\( N \)), and ventilation rate (\( Q_{oa} \)), and select their units.
- Convert ventilation rate to cfm.
- Calculate the steady-state indoor concentration using the formula.
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Steady-State Indoor Pollutant Concentration Calculation
Calculating the steady-state indoor pollutant concentration is crucial for:
- Indoor Air Quality: Predicts pollutant levels to ensure a safe and healthy indoor environment, aiding in compliance with air quality standards.
- HVAC Design: Helps design ventilation systems with adequate fresh air supply to dilute pollutants, optimizing occupant health and comfort.
- Energy Efficiency: Balances ventilation rates to control pollutant levels without over-ventilating, reducing energy consumption.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( N = 0.025 \, \text{cfm} \times 10^6 \, \text{ppm/cfm} \), \( Q_{oa} = 41.67 \, \text{cfm} \), \( C_o = 400 \, \text{ppm} \), concentration in ppm:
- \( N = 0.025 \times 10^6 = 25000 \, \text{ppm·cfm} \)
- \( C_i = 400 + \frac{25000}{41.67} \)
- \( C_i = 400 + 599.952 \approx 999.952 \)
- Since 999.952 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 999.95200 \)
- Example 2: For \( N = 500 \, \text{µg/min} \), \( Q_{oa} = 1 \, \text{m³/s} \), \( C_o = 50 \, \text{µg/ft³} \), concentration in µg/ft³:
- Convert: \( Q_{oa} = 1 \times 2118.88 = 2118.88 \, \text{cfm} \)
- \( C_i = 50 + \frac{500}{2118.88} \)
- \( C_i = 50 + 0.23593 \approx 50.23593 \)
- Since 50.23593 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 50.23593 \)
- Example 3: For \( N = 0.0001 \, \text{ppm·cfm} \), \( Q_{oa} = 100 \, \text{cfm} \), \( C_o = 0.00005 \, \text{ppm} \), concentration in ppm:
- \( C_i = 0.00005 + \frac{0.0001}{100} \)
- \( C_i = 0.00005 + 0.000001 = 0.000051 \)
- Since 0.000051 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.00005 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does steady-state indoor pollutant concentration mean in HVAC systems?
A: Steady-state indoor pollutant concentration (\( C_i \)) refers to the constant concentration of a pollutant in a space when the rates of pollutant generation, ventilation, and removal are balanced, assuming thorough mixing.
Q: Why is thorough mixing assumed in this calculation?
A: Thorough mixing is assumed to simplify the calculation, ensuring the pollutant concentration is uniform throughout the space, which aligns with idealized ventilation models used in HVAC design.
Q: How can I determine the pollutant generation rate for my system?
A: The pollutant generation rate (\( N \)) can be estimated based on the sources of pollutants (e.g., occupants, equipment, materials) in the space, often derived from environmental studies, manufacturer data, or air quality measurements.
Steady-State Indoor Pollutant Concentration Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back