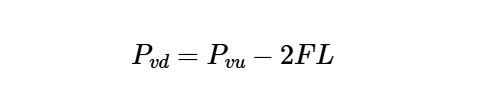1. What is a Static Regain for Duct Sizing Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the downstream velocity pressure (\( P_{v d} \)) in a duct section using the static regain method, assuming 50% efficiency, to size ducts for maintaining constant static pressure.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC design to determine the appropriate downstream duct size to balance static pressure losses, ensuring efficient airflow distribution.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for downstream velocity pressure:
Downstream Velocity Pressure:
\[
P_{v d} = P_{v u} - 2 F L
\]
Where:
- \( P_{v d} \): Velocity pressure in downstream duct (in. of water, Pa)
- \( P_{v u} \): Velocity pressure in upstream duct (in. of water, Pa)
- \( F L \): Friction loss in preceding duct section (in. of water, Pa)
Unit Conversions:
- Velocity Pressure (\( P_{v u} \)) and Friction Loss (\( F L \)): in. of water, Pa (1 Pa = 0.00401463 in. of water)
- Downstream Velocity Pressure (\( P_{v d} \)): in. of water, Pa (1 in. of water = 248.84 Pa)
Steps:
- Enter the upstream velocity pressure (\( P_{v u} \)) and friction loss (\( F L \)), and select their units.
- Convert \( P_{v u} \) and \( F L \) to in. of water.
- Calculate the downstream velocity pressure using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (in. of water or Pa).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Static Regain Calculation
Calculating downstream velocity pressure using the static regain method is crucial for:
- HVAC System Design: Ensures ducts are sized to maintain constant static pressure, balancing airflow across the system.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes duct sizing to minimize pressure losses, reducing fan energy consumption.
- System Performance: Promotes uniform air distribution for effective ventilation and thermal comfort.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( P_{v u} = 1.56 \, \text{in. of water} \), \( F L = 0.35 \, \text{in. of water} \), downstream velocity pressure in in. of water:
- \( P_{v d} = 1.56 - 2 \times 0.35 = 0.86 \)
- Since 0.86 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.86000 \)
- Example 2: For \( P_{v u} = 400 \, \text{Pa} \), \( F L = 80 \, \text{Pa} \), downstream velocity pressure in Pa:
- Convert: \( P_{v u} = 400 \times 0.00401463 \approx 1.605852 \, \text{in. of water} \)
- \( F L = 80 \times 0.00401463 \approx 0.321170 \, \text{in. of water} \)
- \( P_{v d} = 1.605852 - 2 \times 0.321170 \approx 0.963512 \, \text{in. of water} \)
- Convert to Pa: \( 0.963512 \times 248.84 \approx 239.755 \)
- Since 239.755 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 239.75500 \)
- Example 3: For \( P_{v u} = 2.0 \, \text{in. of water} \), \( F L = 0.4 \, \text{in. of water} \), downstream velocity pressure in in. of water:
- \( P_{v d} = 2.0 - 2 \times 0.4 = 1.2 \)
- Since 1.2 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 1.20000 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does downstream velocity pressure represent?
A: Downstream velocity pressure (\( P_{v d} \)) is the velocity pressure in the downstream duct section, calculated to size ducts while maintaining constant static pressure using the static regain method.
Q: How can I determine the upstream velocity pressure and friction loss?
A: Upstream velocity pressure (\( P_{v u} \)) is calculated from the upstream air velocity and density using \( P_v = \rho \left( \frac{V}{4005} \right)^2 \), or obtained from measurements. Friction loss (\( F L \)) is determined from duct friction charts or calculations based on duct length and material.
Q: Why is static regain important in duct sizing?
A: It ensures ducts are sized to balance static pressure losses, promoting efficient airflow and reducing fan energy requirements.
Static Regain for Duct Sizing Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back