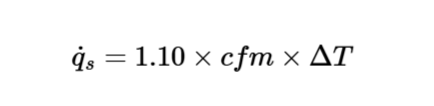1. What is a Sensible Heat Loss Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the sensible heat loss (\( \dot{q}_s \)) due to infiltration air, based on the infiltration air flow rate and the indoor-outdoor temperature difference.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC design to quantify the heat loss caused by cold outdoor air entering a building, aiding in the sizing of heating systems and improving energy efficiency.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for sensible heat loss:
Sensible Heat Loss:
\[
\dot{q}_s = 1.10 \times cfm \times \Delta T
\]
Where:
- \( \dot{q}_s \): Sensible heat loss (Btu/hr, W)
- \( cfm \): Infiltration air flow rate (ft³/min, m³/s)
- \( \Delta T \): Indoor-outdoor temperature difference (°F, °C)
Unit Conversions:
- Air Flow Rate (\( cfm \)): ft³/min, m³/s (1 m³/s = 2118.88 ft³/min)
- Temperature Difference (\( \Delta T \)): °F, °C (ΔT in °F = ΔT in °C × 9/5)
- Sensible Heat Loss (\( \dot{q}_s \)): Btu/hr, W (1 Btu/hr = 0.293071 W)
Steps:
- Enter the infiltration air flow rate (\( cfm \)) and indoor-outdoor temperature difference (\( \Delta T \)), and select their units.
- Convert \( cfm \) to ft³/min and \( \Delta T \) to °F.
- Calculate the sensible heat loss using the formula, with the constant 1.10 Btu/hr per ft³/min-°F.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (Btu/hr or W).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Sensible Heat Loss Calculation
Calculating sensible heat loss is crucial for:
- HVAC Design: Determines the heating load required to offset heat loss from infiltration, aiding in system sizing.
- Energy Efficiency: Helps identify excessive infiltration, guiding improvements in building sealing to reduce energy consumption.
- Thermal Comfort: Ensures indoor temperatures remain comfortable by accounting for heat loss due to incoming cold air.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( cfm = 40 \, \text{ft³/min} \), \( \Delta T = 60 \, \text{°F} \), sensible heat loss in Btu/hr:
- \( \dot{q}_s = 1.10 \times 40 \times 60 = 2640 \)
- Since 2640 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 2640.00000 \)
- Example 2: For \( cfm = 0.01888 \, \text{m³/s} \), \( \Delta T = 15.56 \, \text{°C} \), sensible heat loss in W:
- Convert: \( cfm = 0.01888 \times 2118.88 \approx 40 \, \text{ft³/min} \)
- \( \Delta T = 15.56 \times 9/5 = 28 \, \text{°F} \)
- \( \dot{q}_s = 1.10 \times 40 \times 28 \approx 1232 \, \text{Btu/hr} \)
- Convert to W: \( 1232 \times 0.293071 \approx 361.063 \)
- Since 361.063 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 361.06300 \)
- Example 3: For \( cfm = 100 \, \text{ft³/min} \), \( \Delta T = 50 \, \text{°F} \), sensible heat loss in Btu/hr:
- \( \dot{q}_s = 1.10 \times 100 \times 50 = 5500 \)
- Since 5500 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 5500.00000 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does sensible heat loss due to infiltration represent?
A: Sensible heat loss (\( \dot{q}_s \)) quantifies the heat required to warm cold outdoor air infiltrating a building to the indoor temperature, affecting heating loads.
Q: How can I determine the infiltration air flow rate?
A: The infiltration air flow rate (\( cfm \)) can be estimated using methods like the air change method, crack method, or measured through blower door tests.
Q: Why is sensible heat loss important in HVAC design?
A: It contributes to the heating load, ensuring that HVAC systems are sized correctly to maintain thermal comfort and energy efficiency.
Sensible Heat Loss Due to Infiltration Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back