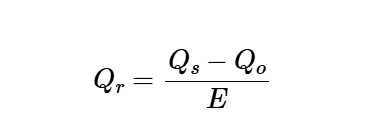1. What is a Recirculation Rate with Filtration Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the recirculation rate (\( Q_r \)) required to reduce the outdoor air ventilation rate in an HVAC system, using a filter with a specified efficiency to maintain indoor air quality.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems as part of the indoor air quality procedure to minimize outdoor air intake while ensuring acceptable air quality through filtration, balancing energy efficiency and occupant health.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for the recirculation rate:
Recirculation Rate:
\[
Q_r = \frac{Q_s - Q_o}{E}
\]
Where:
- \( Q_r \): Recirculation rate (cfm/person, m³/s/person, L/s/person)
- \( Q_s \): Supply air rate (cfm/person, m³/s/person, L/s/person)
- \( Q_o \): Outdoor air rate (cfm/person, m³/s/person, L/s/person)
- \( E \): Filter efficiency (dimensionless, e.g., 0.75 for 75%)
Unit Conversions:
- Air Flow Rates (\( Q_s \), \( Q_o \), \( Q_r \)): cfm/person, m³/s/person (1 cfm = 0.000471947 m³/s), L/s/person (1 cfm = 0.471947 L/s)
Steps:
- Enter the supply air rate (\( Q_s \)), outdoor air rate (\( Q_o \)), and filter efficiency (\( E \)), and select their units.
- Convert air flow rates to cfm/person.
- Calculate the recirculation rate using the formula (result in cfm/person).
- Convert the result to the selected unit (cfm/person, m³/s/person, or L/s/person).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Recirculation Rate with Filtration Calculation
Calculating the recirculation rate with filtration is crucial for:
- Indoor Air Quality: Ensures acceptable air quality by filtering recirculated air, reducing the need for excessive outdoor air intake.
- Energy Efficiency: Minimizes outdoor air ventilation, reducing heating and cooling loads, especially in extreme climates, while maintaining air quality through filtration.
- HVAC Design: Helps design systems that balance fresh air intake with recirculation and filtration, optimizing system performance and occupant comfort.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( Q_s = 60 \, \text{cfm/person} \), \( Q_o = 15 \, \text{cfm/person} \), \( E = 0.75 \), recirculation rate in cfm/person:
- \( Q_r = \frac{60 - 15}{0.75} \)
- \( Q_r = \frac{45}{0.75} = 60.00000 \)
- Since 60.00000 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 60.00000 \)
- Example 2: For \( Q_s = 0.05 \, \text{m³/s/person} \), \( Q_o = 0.01 \, \text{m³/s/person} \), \( E = 0.80 \), recirculation rate in m³/s/person:
- Convert: \( Q_s = 0.05 \times 2118.88 = 105.944 \, \text{cfm/person} \), \( Q_o = 0.01 \times 2118.88 = 21.1888 \, \text{cfm/person} \)
- \( Q_r = \frac{105.944 - 21.1888}{0.80} \)
- \( Q_r = \frac{84.7552}{0.80} \approx 105.94400 \, \text{cfm/person} \)
- Convert to m³/s/person: \( 105.94400 \times 0.000471947 = 0.05000 \)
- Since 0.05000 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.05000 \)
- Example 3: For \( Q_s = 1 \, \text{L/s/person} \), \( Q_o = 0.2 \, \text{L/s/person} \), \( E = 0.90 \), recirculation rate in L/s/person:
- Convert: \( Q_s = 1 \times 2.11888 = 2.11888 \, \text{cfm/person} \), \( Q_o = 0.2 \times 2.11888 = 0.423776 \, \text{cfm/person} \)
- \( Q_r = \frac{2.11888 - 0.423776}{0.90} \)
- \( Q_r = \frac{1.695104}{0.90} \approx 1.88345 \, \text{cfm/person} \)
- Convert to L/s/person: \( 1.88345 \times 0.471947 \approx 0.88889 \)
- Since 0.88889 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.88889 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the recirculation rate in HVAC systems?
A: The recirculation rate (\( Q_r \)) in HVAC systems is the rate at which indoor air is recirculated through the system, often filtered, to reduce the amount of outdoor air needed while maintaining indoor air quality.
Q: Why is filter efficiency important in this calculation?
A: Filter efficiency (\( E \)) determines how effectively the filter removes pollutants from the recirculated air. Higher efficiency reduces the required recirculation rate to achieve the same air quality, impacting system design and energy use.
Q: How can I determine the supply and outdoor air rates for my system?
A: Supply air rate (\( Q_s \)) and outdoor air rate (\( Q_o \)) can be determined based on HVAC design standards (e.g., ASHRAE guidelines), occupant density, and ventilation requirements, often calculated per person for a given space.
Recirculation Rate with Filtration Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back