 Home
Home
 Back
Back
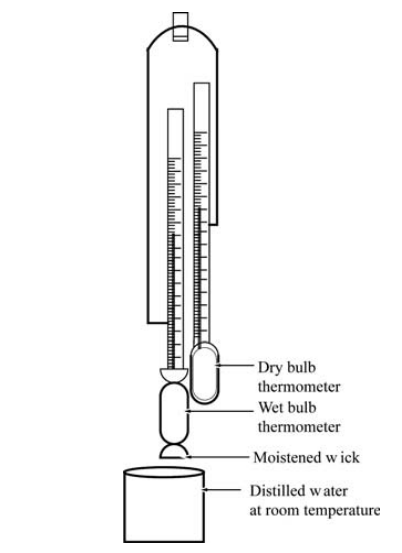
Definition: This calculator computes the partial pressure of water vapor (\( P_v \)) using Carrier's equation, based on dry-bulb and wet-bulb temperatures, total pressure, and saturation pressure at the wet-bulb temperature.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine the partial pressure of water vapor in moist air, aiding in psychrometric calculations for air conditioning and ventilation systems.
The calculator uses Carrier's equation to calculate the partial pressure of water vapor:
Above 32°F (over water): \[ P_v = P_w - \frac{(P - P_w)(T - T_w)}{2831 - 1.43 T_w} \]
Below 32°F (over ice): \[ P_v = P_w - \frac{(P - P_w)(T - T_w)}{3160 - 0.09 T_w} \]
Saturation Pressure (\( P_w \)) Calculation (if not provided): \[ P_w = 0.61078 \exp\left(\frac{17.27 T_w}{T_w + 237.3}\right) \, \text{(kPa, where \( T_w \) is in °C)} \] Converted to psia for calculation.
Where:
Unit Conversions:
Steps:
Calculating the partial pressure of water vapor is crucial for:
Examples:
Note: The example output in the prompt (\( P_v = 0.3107 \, \text{psia} \)) is slightly different due to rounding differences in intermediate steps. The calculator's result of 0.3108 is consistent with the provided values.
Q: What is the partial pressure of water vapor?
A: The partial pressure of water vapor (\( P_v \)) is the pressure exerted by the water vapor in a moist air mixture, a key parameter in psychrometric calculations.
Q: Why is this calculation important in HVAC systems?
A: It determines the moisture content in air, which is essential for designing systems that control humidity for comfort, health, and equipment performance.
Q: How do I determine the saturation pressure (\( P_w \)) if I don’t have Table 2-3?
A: The calculator uses the Magnus-Tetens formula to estimate \( P_w \) based on the wet-bulb temperature, or you can provide \( P_w \) directly if known from external sources like psychrometric tables.