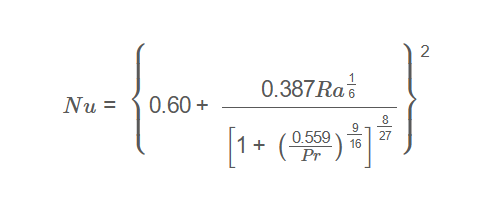1. What is a Natural Convection (Horizontal Cylinder) Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the Prandtl number (\( Pr \)), Grashof number (\( Gr \)), Rayleigh number (\( Ra \)), and Nusselt number (\( Nu \)) for natural convection over a horizontal cylinder, valid for \( Ra < 10^{12} \).
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine heat transfer coefficients (\( h \)) for pipes or tubes, optimizing natural convection heat transfer.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas for natural convection over a horizontal cylinder:
Prandtl Number:
\[
Pr = \frac{\mu}{\rho \alpha}
\]
Grashof Number:
\[
Gr = \frac{L^3 \rho^2 \beta g \Delta T}{\mu^2}
\]
Rayleigh Number:
\[
Ra = Gr Pr
\]
Nusselt Number:
\[
Nu = \left\{ 0.60 + \frac{0.387 Ra^{\frac{1}{6}}}{\left[ 1 + \left( \frac{0.559}{Pr} \right)^{\frac{9}{16}} \right]^{\frac{8}{27}}} \right\}^2
\]
Where:
- \( Nu \): Nusselt number (dimensionless)
- \( Pr \): Prandtl number (dimensionless)
- \( Gr \): Grashof number (dimensionless)
- \( Ra \): Rayleigh number (dimensionless)
- \( L \): Characteristic length (ft, in, m, e.g., diameter of the horizontal cylinder)
- \( \rho \): Fluid density (lb/ft³, kg/m³)
- \( \beta \): Thermal expansion coefficient (1/°F, 1/°C)
- \( g \): Gravitational acceleration (32.174 ft/s²)
- \( \Delta T \): Temperature difference (\( |T_{\text{surface}} - T_{\text{fluid}}| \), °F, °C)
- \( \mu \): Dynamic viscosity (lb/ft-s, Pa-s)
- \( \alpha \): Thermal diffusivity (ft²/s, m²/s)
Unit Conversions:
- Characteristic Length (\( L \)): ft, in (1 in = \( \frac{1}{12} \) ft), m (1 m = 3.28084 ft)
- Fluid Density (\( \rho \)): lb/ft³, kg/m³ (1 kg/m³ = 0.062428 lb/ft³)
- Thermal Expansion Coefficient (\( \beta \)): 1/°F, 1/°C (1/°C = (9/5)/°F)
- Temperature Difference (\( \Delta T \)): °F, °C (1 °C = (9/5) °F)
- Dynamic Viscosity (\( \mu \)): lb/ft-s, Pa-s (1 Pa-s = 0.671969 lb/ft-s)
- Thermal Diffusivity (\( \alpha \)): ft²/s, m²/s (1 m²/s = 10.7639 ft²/s)
Steps:
- Enter the characteristic length (\( L \)), fluid density (\( \rho \)), thermal expansion coefficient (\( \beta \)), temperature difference (\( \Delta T \)), dynamic viscosity (\( \mu \)), and thermal diffusivity (\( \alpha \)), and select their units.
- Convert all inputs to base units (\( L \) to ft, \( \rho \) to lb/ft³, \( \beta \) to 1/°F, \( \Delta T \) to °F, \( \mu \) to lb/ft-s, \( \alpha \) to ft²/s).
- Calculate the Prandtl number using \( Pr = \frac{\mu}{\rho \alpha} \).
- Calculate the Grashof number using \( Gr = \frac{L^3 \rho^2 \beta g \Delta T}{\mu^2} \).
- Calculate the Rayleigh number using \( Ra = Gr Pr \).
- Validate that \( Ra < 10^{12} \).
- Calculate the Nusselt number using the given formula.
- Display \( Pr \), \( Gr \), \( Ra \), and \( Nu \), using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Natural Convection (Horizontal Cylinder) Calculation
Calculating the Nusselt number for natural convection over a horizontal cylinder is crucial for:
- HVAC Design: Determines heat transfer coefficients for pipes or tubes, optimizing natural convection heat transfer in HVAC systems.
- Energy Efficiency: Helps design systems that efficiently transfer heat via natural convection, reducing energy consumption.
- System Performance: Ensures accurate thermal load calculations for heating and cooling systems.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the natural convection correlation for a horizontal cylinder?
A: The correlation \( Nu = \left\{ 0.60 + \frac{0.387 Ra^{\frac{1}{6}}}{\left[ 1 + \left( \frac{0.559}{Pr} \right)^{\frac{9}{16}} \right]^{\frac{8}{27}}} \right\}^2 \) calculates the Nusselt number for natural convection over a horizontal cylinder, valid for \( Ra < 10^{12} \).
Q: Why is this calculation important in HVAC systems?
A: It determines heat transfer coefficients for pipes or tubes, optimizing natural convection heat transfer in HVAC systems.
Q: How do I determine the characteristic length (\( L \))?
A: For a horizontal cylinder, the characteristic length (\( L \)) is typically the diameter of the cylinder.
Natural Convection (Horizontal Cylinder) Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back