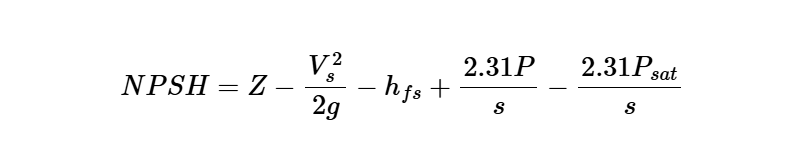1. What is a Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the net positive suction head (\( NPSH \)) available at the suction side of a centrifugal pump, ensuring sufficient pressure to prevent cavitation, based on vertical distance (\( Z \)), suction line velocity (\( V_s \)), gravity (\( g \)), suction line friction head (\( h_{fs} \)), liquid surface pressure (\( P \)), saturation pressure (\( P_{sat} \)), and specific gravity (\( s \)).
Purpose: It is used in pump system design to verify that the NPSH available exceeds the NPSH required by the pump, preventing cavitation, ensuring reliable operation, and extending pump life.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for NPSH:
Net Positive Suction Head:
\[
NPSH = Z - \frac{V_s^2}{2 g} - h_{fs} + \frac{2.31 P}{s} - \frac{2.31 P_{sat}}{s}
\]
Where:
- \( NPSH \): Net positive suction head (ft, m)
- \( Z \): Vertical distance from source to pump centerline (ft, m)
- \( V_s \): Suction line velocity (ft/s, m/s)
- \( g \): Acceleration of gravity (ft/s², m/s²)
- \( h_{fs} \): Suction line friction head (ft, m)
- \( P \): Liquid surface pressure (psia, Pa)
- \( P_{sat} \): Saturation pressure (psia, Pa)
- \( s \): Specific gravity (dimensionless)
Unit Conversions:
- Distance and Head (\( Z \), \( h_{fs} \), \( NPSH \)): ft, m (1 m = 3.28084 ft; 1 ft = 0.3048 m)
- Velocity (\( V_s \)): ft/s, m/s (1 m/s = 3.28084 ft/s)
- Gravity (\( g \)): ft/s², m/s² (1 m/s² = 3.28084 ft/s²)
- Pressure (\( P \), \( P_{sat} \)): psia, Pa (1 Pa = 0.000145038 psia)
Steps:
- Enter the vertical distance (\( Z \)), suction line velocity (\( V_s \)), acceleration of gravity (\( g \)), suction line friction head (\( h_{fs} \)), liquid surface pressure (\( P \)), saturation pressure (\( P_{sat} \)), and specific gravity (\( s \)), and select their units.
- Convert \( Z \) and \( h_{fs} \) to ft, \( V_s \) to ft/s, \( g \) to ft/s², and \( P \), \( P_{sat} \) to psia.
- Calculate NPSH using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (ft or m).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of NPSH Calculation
Calculating the NPSH is crucial for:
- Pump System Safety: Prevents cavitation, which can damage pump components and reduce efficiency.
- Pump Selection: Ensures the pump operates with sufficient NPSH to meet system requirements, avoiding performance issues.
- System Reliability: Supports stable pump operation by maintaining adequate suction pressure, extending equipment lifespan.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( Z = -5 \, \text{ft} \), \( V_s = 2 \, \text{ft/s} \), \( g = 32.2 \, \text{ft/s²} \), \( h_{fs} = 0.91 \, \text{ft} \), \( P = 14.7 \, \text{psia} \), \( P_{sat} = 0.36 \, \text{psia} \), \( s = 1.00 \), NPSH in ft:
- \( NPSH = -5 - \frac{2^2}{2 \times 32.2} - 0.91 + \frac{2.31 \times 14.7}{1.00} - \frac{2.31 \times 0.36}{1.00} \)
- \( = -5 - \frac{4}{64.4} - 0.91 + 33.957 - 0.8316 \approx -5 - 0.06211 - 0.91 + 33.957 - 0.8316 \approx 27.153 \)
- Since 27.153 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 27.15300 \)
- Note: The calculated value (27.153 ft) is close to the example output of 27.16 ft, with minor differences likely due to rounding in the original example.
- Example 2: For \( Z = -1.524 \, \text{m} \), \( V_s = 0.6096 \, \text{m/s} \), \( g = 9.81 \, \text{m/s²} \), \( h_{fs} = 0.2774 \, \text{m} \), \( P = 101325 \, \text{Pa} \), \( P_{sat} = 2482.11 \, \text{Pa} \), \( s = 1.00 \), NPSH in m:
- Convert: \( Z = -1.524 \times 3.28084 \approx -5 \, \text{ft} \)
- \( V_s = 0.6096 \times 3.28084 \approx 2 \, \text{ft/s} \)
- \( g = 9.81 \times 3.28084 \approx 32.2 \, \text{ft/s²} \)
- \( h_{fs} = 0.2774 \times 3.28084 \approx 0.91 \, \text{ft} \)
- \( P = 101325 \times 0.000145038 \approx 14.7 \, \text{psia} \)
- \( P_{sat} = 2482.11 \times 0.000145038 \approx 0.36 \, \text{psia} \)
- \( NPSH = -5 - \frac{2^2}{2 \times 32.2} - 0.91 + \frac{2.31 \times 14.7}{1.00} - \frac{2.31 \times 0.36}{1.00} \approx 27.153 \, \text{ft} \)
- Convert to m: \( 27.153 \times 0.3048 \approx 8.276 \)
- Since 8.276 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 8.27600 \)
- Example 3: For \( Z = -3 \, \text{ft} \), \( V_s = 3 \, \text{ft/s} \), \( g = 32.2 \, \text{ft/s²} \), \( h_{fs} = 1.5 \, \text{ft} \), \( P = 15 \, \text{psia} \), \( P_{sat} = 0.5 \, \text{psia} \), \( s = 0.85 \), NPSH in ft:
- \( NPSH = -3 - \frac{3^2}{2 \times 32.2} - 1.5 + \frac{2.31 \times 15}{0.85} - \frac{2.31 \times 0.5}{0.85} \)
- \( = -3 - \frac{9}{64.4} - 1.5 + 40.765 - 1.359 \approx -3 - 0.13975 - 1.5 + 40.765 - 1.359 \approx 34.766 \)
- Since 34.766 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 34.76600 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does net positive suction head (NPSH) represent?
A: NPSH represents the absolute pressure head available at the pump suction above the vapor pressure of the liquid, ensuring the pump operates without cavitation, which can cause damage and reduce efficiency.
Q: How can I determine the input parameters?
A: Vertical distance (\( Z \)) is measured from the liquid source to the pump centerline (e.g., -5 ft for suction lift). Suction line velocity (\( V_s \)) is calculated from flow rate and pipe diameter (e.g., 2 ft/s). Acceleration of gravity (\( g \)) is typically 32.2 ft/s² or 9.81 m/s². Suction line friction head (\( h_{fs} \)) is determined from pipe losses (e.g., 0.91 ft). Liquid surface pressure (\( P \)) is the pressure at the source (e.g., 14.7 psia for atmospheric). Saturation pressure (\( P_{sat} \)) is obtained from liquid properties at the operating temperature (e.g., 0.36 psia for water at a given temperature). Specific gravity (\( s \)) is the liquid’s density relative to water (e.g., 1.00 for water).
Q: Why is NPSH calculation important in pump system design?
A: It ensures the pump operates with sufficient suction pressure to prevent cavitation, optimizing performance, preventing damage, and ensuring reliable and efficient system operation.
Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back