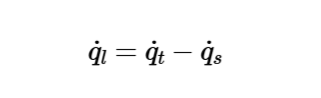1. What is a Latent Heat Load Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the latent heat load (\( \dot{q}_l \)) by subtracting the sensible heat load from the total heat load in a cooling or heating process.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine the latent heat load, which represents the energy required to change the humidity level of the air, aiding in the design of air conditioning systems for humidity control.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for the latent heat load:
Latent Heat Load:
\[
\dot{q}_l = \dot{q}_t - \dot{q}_s
\]
Where:
- \( \dot{q}_l \): Latent heat load (Btu/hr, convertible to kW)
- \( \dot{q}_t \): Total heat load (Btu/hr, kW)
- \( \dot{q}_s \): Sensible heat load (Btu/hr, kW)
Unit Conversions:
- Heat Loads (\( \dot{q}_t \), \( \dot{q}_s \), \( \dot{q}_l \)): Btu/hr, kW (1 kW = 3412.14 Btu/hr, 1 Btu/hr = 0.000293071 kW)
Steps:
- Enter the total heat load (\( \dot{q}_t \)) and sensible heat load (\( \dot{q}_s \)), and select their units.
- Convert heat loads to Btu/hr.
- Calculate the latent heat load using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (Btu/hr or kW).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Latent Heat Load Calculation
Calculating the latent heat load is crucial for:
- HVAC Design: Determines the energy required to manage humidity, aiding in the sizing of dehumidification or humidification equipment.
- Energy Efficiency: Helps optimize system performance by ensuring the correct balance between sensible and latent heat management.
- System Performance: Ensures the system can achieve the desired humidity levels for comfort or process requirements by accurately calculating the latent heat load.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( \dot{q}_t = 110000 \, \text{Btu/hr} \), \( \dot{q}_s = 88000 \, \text{Btu/hr} \), latent heat load in Btu/hr:
- \( \dot{q}_l = 110000 - 88000 = 22000.00000 \)
- Since 22000.00000 > 10000, use scientific notation: \( 2.20000e+4 \)
- Example 2: For \( \dot{q}_t = 70 \, \text{kW} \), \( \dot{q}_s = 50 \, \text{kW} \), latent heat load in kW:
- Convert: \( \dot{q}_t = 70 \times 3412.14 = 238849.8 \, \text{Btu/hr} \), \( \dot{q}_s = 50 \times 3412.14 = 170607 \, \text{Btu/hr} \)
- \( \dot{q}_l = 238849.8 - 170607 = 68242.80000 \, \text{Btu/hr} \)
- Convert to kW: \( 68242.80000 \times 0.000293071 = 20.00000 \)
- Since 20.00000 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 20.00000 \)
- Example 3: For \( \dot{q}_t = 0.0001 \, \text{Btu/hr} \), \( \dot{q}_s = 0.00008 \, \text{Btu/hr} \), latent heat load in Btu/hr:
- \( \dot{q}_l = 0.0001 - 0.00008 = 0.00002 \)
- Since 0.00002 < 0.00001, use scientific notation: \( 2.00000e-5 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the latent heat load in HVAC systems?
A: The latent heat load (\( \dot{q}_l \)) in HVAC systems is the energy required to change the humidity level of the air, such as through condensation (dehumidification) or evaporation (humidification), without changing the temperature.
Q: Why is the latent heat load important?
A: The latent heat load is important because it quantifies the energy needed to manage humidity, which is critical for comfort, indoor air quality, and specific process requirements in HVAC systems.
Q: How can I determine the total and sensible heat loads for my system?
A: Total and sensible heat loads can be calculated using psychrometric equations, measured using HVAC design software, or estimated based on temperature and humidity changes in the air stream, often derived from psychrometric charts or field measurements.
Latent Heat Load Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back