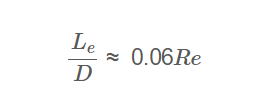1. What is a Laminar Flow Entrance Length Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the entrance length (\( L_e \)) required for laminar flow to become fully developed in a pipe or duct, using the Reynolds number and duct diameter.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine the duct length needed for stable, fully developed laminar flow, ensuring accurate pressure drop and flow calculations.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the laminar flow entrance length formula:
Entrance Length:
\[
\frac{L_e}{D} \approx 0.06 Re
\]
Where:
- \( L_e \): Entrance length (ft, in, m)
- \( D \): Pipe or duct diameter (ft, in, m)
- \( Re \): Reynolds number (dimensionless), \( Re = \frac{\rho V
- \( \rho \): Fluid density (lb/ft³, kg/m³)
- \( V \): Average velocity (ft/s, m/s)
- \( D \): Pipe or duct diameter (ft, in, m)
- \( \mu \): Dynamic viscosity (lb/ft-s, Pa-s)
Unit Conversions:
- Fluid Density (\( \rho \)): lb/ft³, kg/m³ (1 kg/m³ = 0.062428 lb/ft³)
- Average Velocity (\( V \)): ft/s, m/s (1 m/s = 3.28084 ft/s)
- Diameter (\( D \)) and Entrance Length (\( L_e \)): ft, in (1 in = \( \frac{1}{12} \) ft), m (1 m = 3.28084 ft)
- Dynamic Viscosity (\( \mu \)): lb/ft-s, Pa-s (1 Pa-s = 0.671969 lb/ft-s)
Steps:
- Enter the fluid density, average velocity, diameter, and dynamic viscosity, and select their units.
- Convert all inputs to base units (lb/ft³ for density, ft/s for velocity, ft for diameter, lb/ft-s for viscosity).
- Calculate the Reynolds number using \( Re = \frac{\rho V D}{\mu} \).
- Verify that the flow is laminar (Re < 2300 for HVAC ducts).
- Calculate the entrance length using \( L_e = 0.06 \times Re \times D \).
- Convert the result to the selected unit (ft, in, m).
- Display the result, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Laminar Flow Entrance Length Calculation
Calculating the entrance length for laminar flow is crucial for:
- HVAC Design: Ensures ducts are long enough for fully developed flow, improving the accuracy of pressure drop calculations.
- Flow Stability: Helps achieve stable laminar flow, reducing unexpected turbulence in HVAC systems.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes duct design to minimize energy losses due to undeveloped flow regions.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( \rho = 0.075 \, \text{lb/ft}^3 \), \( V = 5 \, \text{ft/s} \), \( D = 0.5 \, \text{ft} \), \( \mu = 1.2 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{lb/ft-s} \), entrance length in ft:
- Reynolds Number: \( Re = \frac{0.075 \times 5 \times 0.5}{1.2 \times 10^{-5}} = 15625 \)
- Error: Reynolds number (15625) is too high for laminar flow (Re < 2300).
- Example 2: For \( \rho = 1.2 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \), \( V = 0.5 \, \text{m/s} \), \( D = 0.1 \, \text{m} \), \( \mu = 1.8 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{Pa-s} \), entrance length in m:
- Convert: \( \rho = 1.2 \times 0.062428 = 0.0749136 \, \text{lb/ft}^3 \), \( V = 0.5 \times 3.28084 = 1.64042 \, \text{ft/s} \), \( D = 0.1 \times 3.28084 = 0.328084 \, \text{ft} \), \( \mu = 1.8 \times 10^{-5} \times 0.671969 = 1.20954 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{lb/ft-s} \)
- Reynolds Number: \( Re = \frac{0.0749136 \times 1.64042 \times 0.328084}{1.20954 \times 10^{-5}} \approx 3333.33 \)
- Error: Reynolds number (3333.33) is too high for laminar flow (Re < 2300).
- Example 3 (Valid Laminar Flow): For \( \rho = 0.075 \, \text{lb/ft}^3 \), \( V = 0.1 \, \text{ft/s} \), \( D = 0.2 \, \text{ft} \), \( \mu = 1.2 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{lb/ft-s} \), entrance length in ft:
- Reynolds Number: \( Re = \frac{0.075 \times 0.1 \times 0.2}{1.2 \times 10^{-5}} = 125 \)
- Entrance Length: \( L_e = 0.06 \times 125 \times 0.2 = 1.5000 \, \text{ft} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the entrance length in laminar flow?
A: The entrance length (\( L_e \)) is the distance required for laminar flow to become fully developed in a pipe or duct, approximated as \( \frac{L_e}{D} \approx 0.06 Re \).
Q: Why is entrance length important in HVAC systems?
A: It ensures that the flow is fully developed, allowing for accurate pressure drop calculations and efficient duct design in HVAC systems.
Q: How do I know if the flow is laminar?
A: Calculate the Reynolds number (\( Re \)). For HVAC ducts, flow is typically laminar if \( Re < 2300 \).
Laminar Flow Entrance Length Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back