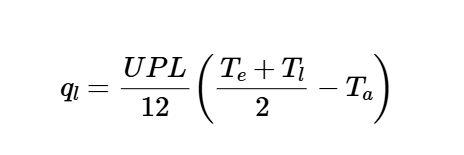1. What is a Heat Loss/Gain Through Duct Walls Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the heat loss or gain (\( q_l \)) through duct walls, accounting for the overall heat transfer coefficient, duct dimensions, and temperature differences in HVAC systems.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC design to quantify the heat transfer between ducted air and the surrounding environment, aiding in system sizing and energy efficiency.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for heat loss/gain:
Heat Loss/Gain:
\[
q_l = \frac{U P L}{12} \left( \frac{T_e + T_l}{2} - T_a \right)
\]
Where:
- \( q_l \): Heat loss/gain through duct walls (Btu/hr, W; negative for heat gain)
- \( U \): Overall heat transfer coefficient (Btu/hr-ft²-°F, W/m²-K)
- \( P \): Perimeter of bare or insulated duct (in., ft, m)
- \( L \): Duct length (ft, m)
- \( T_e \): Temperature of air entering duct (°F, °C)
- \( T_l \): Temperature of air leaving duct (°F, °C)
- \( T_a \): Temperature of air surrounding duct (°F, °C)
Unit Conversions:
- Heat Transfer Coefficient (\( U \)): Btu/hr-ft²-°F, W/m²-K (1 W/m²-K = 0.176110 Btu/hr-ft²-°F)
- Perimeter (\( P \)):
- in.: No conversion
- ft: 1 ft = 12 in.
- m: 1 m = 39.3701 in.
- Duct Length (\( L \)): ft, m (1 m = 3.28084 ft)
- Temperatures (\( T_e \), \( T_l \), \( T_a \)): °F, °C (°F = °C × 9/5 + 32)
- Heat Loss/Gain (\( q_l \)): Btu/hr, W (1 Btu/hr = 0.293071 W)
Steps:
- Enter the overall heat transfer coefficient (\( U \)), perimeter (\( P \)), duct length (\( L \)), entering air temperature (\( T_e \)), leaving air temperature (\( T_l \)), and surrounding air temperature (\( T_a \)), and select their units.
- Convert \( U \) to Btu/hr-ft²-°F, \( P \) to in., \( L \) to ft, and temperatures to °F.
- Calculate the heat loss/gain using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (Btu/hr or W).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Heat Loss/Gain Calculation
Calculating heat loss or gain through duct walls is crucial for:
- HVAC System Design: Determines the thermal load on the system, ensuring accurate sizing of heating or cooling equipment.
- Energy Efficiency: Guides insulation choices to minimize unwanted heat transfer, reducing energy consumption.
- Thermal Comfort: Maintains desired air temperatures for occupant comfort.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( U = 0.73 \, \text{Btu/hr-ft²-°F} \), \( P = 84 \, \text{in.} \), \( L = 40 \, \text{ft} \), \( T_e = 131.10 \, \text{°F} \), \( T_l = 122 \, \text{°F} \), \( T_a = 40 \, \text{°F} \), heat loss in Btu/hr:
- \( \frac{T_e + T_l}{2} = \frac{131.10 + 122}{2} = 126.55 \)
- \( 126.55 - 40 = 86.55 \)
- \( q_l = \frac{0.73 \times 84 \times 40}{12} \times 86.55 \approx 204.4 \times 86.55 \approx 17690.82 \)
- Since 17690.82 > 10000, display in scientific notation: \( 1.76908 \times 10^4 \)
- Example 2: For \( U = 4.1 \, \text{W/m²-K} \), \( P = 2.1 \, \text{m} \), \( L = 12 \, \text{m} \), \( T_e = 55 \, \text{°C} \), \( T_l = 50 \, \text{°C} \), \( T_a = 4.4 \, \text{°C} \), heat loss in W:
- Convert: \( U = 4.1 \times 0.176110 \approx 0.722051 \, \text{Btu/hr-ft²-°F} \)
- \( P = 2.1 \times 39.3701 \approx 82.67721 \, \text{in.} \)
- \( L = 12 \times 3.28084 \approx 39.37008 \, \text{ft} \)
- \( T_e = 55 \times 9/5 + 32 = 131 \, \text{°F} \), \( T_l = 50 \times 9/5 + 32 = 122 \, \text{°F} \), \( T_a = 4.4 \times 9/5 + 32 = 39.92 \, \text{°F} \)
- \( \frac{131 + 122}{2} = 126.5 \), \( 126.5 - 39.92 = 86.58 \)
- \( q_l = \frac{0.722051 \times 82.67721 \times 39.37008}{12} \times 86.58 \approx 195.773 \times 86.58 \approx 16948.0 \, \text{Btu/hr} \)
- Convert to W: \( 16948.0 \times 0.293071 \approx 4966.77 \)
- Since 4966.77 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 4966.77000 \)
- Example 3: For \( U = 0.5 \, \text{Btu/hr-ft²-°F} \), \( P = 7 \, \text{ft} \), \( L = 50 \, \text{ft} \), \( T_e = 100 \, \text{°F} \), \( T_l = 95 \, \text{°F} \), \( T_a = 80 \, \text{°F} \), heat loss in Btu/hr:
- Convert: \( P = 7 \times 12 = 84 \, \text{in.} \)
- \( \frac{100 + 95}{2} = 97.5 \), \( 97.5 - 80 = 17.5 \)
- \( q_l = \frac{0.5 \times 84 \times 50}{12} \times 17.5 \approx 175 \times 17.5 = 3062.5 \)
- Since 3062.5 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 3062.50000 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does heat loss/gain through duct walls represent?
A: Heat loss/gain (\( q_l \)) quantifies the thermal energy transferred between the air inside a duct and the surrounding environment, affecting HVAC system performance.
Q: How can I determine the input parameters?
A: The heat transfer coefficient (\( U \)) is obtained from material properties or standards. Perimeter (\( P \)) and length (\( L \)) are measured from duct dimensions. Temperatures (\( T_e \), \( T_l \), \( T_a \)) are measured or estimated based on system conditions.
Q: Why is heat loss/gain important in HVAC design?
A: It impacts the thermal load, ensuring proper sizing of HVAC equipment and insulation to maintain energy efficiency and comfort.
Heat Loss/Gain Through Duct Walls Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back