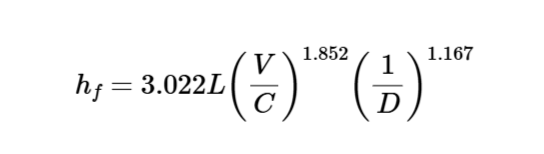1. What is a Head Loss (Hazen-Williams) Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the head loss (\( h_f \)) in a pipe using the Hazen-Williams equation in head form, representing the energy loss due to friction as a height of fluid column.
Purpose: It is used in fluid dynamics, particularly for water distribution and sprinkler systems, to quantify energy losses, aiding in pipe sizing and pump selection.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for head loss:
Head Loss:
\[
h_f = 3.022 L \left( \frac{V}{C} \right)^{1.852} \left( \frac{1}{D} \right)^{1.167}
\]
Where:
- \( h_f \): Head loss (ft, m)
- \( L \): Length of pipe (ft, m)
- \( V \): Average velocity (fps, m/s)
- \( C \): Roughness factor (dimensionless)
- \( D \): Internal diameter of pipe (ft, m)
Unit Conversions:
- Length (\( L \)) and Diameter (\( D \)): ft, m (1 m = 3.28084 ft)
- Velocity (\( V \)): fps, m/s (1 m/s = 3.28084 fps)
- Head Loss (\( h_f \)): ft, m (1 ft = 0.3048 m)
Steps:
- Enter the length of pipe (\( L \)), average velocity (\( V \)), roughness factor (\( C \)), and internal diameter (\( D \)), and select their units.
- Convert \( L \), \( V \), and \( D \) to ft, fps, and ft, respectively.
- Calculate the head loss using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (ft or m).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Head Loss Calculation
Calculating head loss using the Hazen-Williams equation is crucial for:
- Water System Design: Ensures adequate energy for water flow in sprinkler systems and distribution networks.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes pipe sizing to minimize friction losses, reducing pump energy requirements.
- System Performance: Maintains proper flow rates for effective system operation.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( L = 100 \, \text{ft} \), \( V = 4 \, \text{fps} \), \( C = 140 \), \( D = 0.1667 \, \text{ft} \), head loss in ft:
- \( h_f = 3.022 \times 100 \times \left( \frac{4}{140} \right)^{1.852} \times \left( \frac{1}{0.1667} \right)^{1.167} \approx 3.022 \times 100 \times 0.001134 \times 7.987 \approx 136.1 \)
- Since 136.1 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 136.10000 \)
- Example 2: For \( L = 30 \, \text{m} \), \( V = 1.2 \, \text{m/s} \), \( C = 130 \), \( D = 0.05 \, \text{m} \), head loss in m:
- Convert: \( L = 30 \times 3.28084 \approx 98.4252 \, \text{ft} \)
- \( V = 1.2 \times 3.28084 \approx 3.93701 \, \text{fps} \)
- \( D = 0.05 \times 3.28084 \approx 0.164042 \, \text{ft} \)
- \( h_f = 3.022 \times 98.4252 \times \left( \frac{3.93701}{130} \right)^{1.852} \times \left( \frac{1}{0.164042} \right)^{1.167} \approx 297.342 \times 0.001372 \times 8.019 \approx 327.2 \)
- Convert to m: \( 327.2 \times 0.3048 \approx 99.74 \)
- Since 99.74 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 99.74000 \)
- Example 3: For \( L = 50 \, \text{ft} \), \( V = 5 \, \text{fps} \), \( C = 150 \), \( D = 0.25 \, \text{ft} \), head loss in ft:
- \( h_f = 3.022 \times 50 \times \left( \frac{5}{150} \right)^{1.852} \times \left( \frac{1}{0.25} \right)^{1.167} \approx 151.1 \times 0.001937 \times 4.668 \approx 1.366 \)
- Since 1.366 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 1.36600 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does head loss in the Hazen-Williams equation represent?
A: Head loss (\( h_f \)) quantifies the energy loss due to friction in a pipe, expressed as the equivalent height of fluid column, critical for water-based systems.
Q: How can I determine the input parameters?
A: Pipe length (\( L \)) and diameter (\( D \)) are measured. Average velocity (\( V \)) is calculated from flow rate and pipe area. Roughness factor (\( C \)) is obtained from tables based on pipe material (e.g., 140 for smooth pipes).
Q: Why is head loss important in pipe system design?
A: It ensures proper sizing of pipes and pumps to maintain desired flow rates, optimizing energy efficiency and system performance.
Head Loss (Hazen-Williams) Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back