 Home
Home
 Back
Back
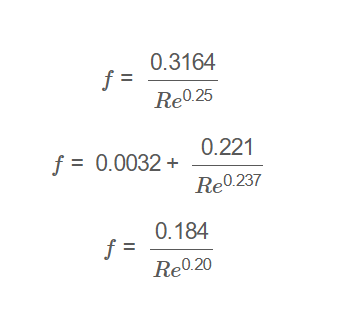
Definition: This calculator computes the friction factor (\( f \)) for turbulent flow in smooth pipes, using empirical correlations based on the Reynolds number.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine the friction factor for calculating pressure losses in ducts, essential for efficient system design.
The calculator uses the following empirical correlations for turbulent flow in smooth pipes:
For \( Re < 10^5 \): \[ f = \frac{0.3164}{Re^{0.25}} \]
For \( 10^5 \leq Re \leq 3 \times 10^6 \): \[ f = 0.0032 + \frac{0.221}{Re^{0.237}} \]
For \( Re > 3 \times 10^6 \): \[ f = \frac{0.184}{Re^{0.20}} \]
Where:
Steps:
Calculating the friction factor for turbulent flow in smooth pipes is crucial for:
Examples:
Q: What is the friction factor in turbulent flow for smooth pipes?
A: The friction factor (\( f \)) is a dimensionless quantity used to calculate pressure losses in turbulent flow through smooth pipes, determined using empirical correlations based on the Reynolds number.
Q: Why is the friction factor important in HVAC systems?
A: It is essential for calculating pressure drops in ducts, ensuring efficient design and operation of HVAC systems in turbulent flow conditions.
Q: How do I determine if the flow is turbulent?
A: The flow is turbulent if the Reynolds number (\( Re \)) is greater than 2300. This calculator assumes turbulent flow and applies the appropriate formula based on the \( Re \) range.