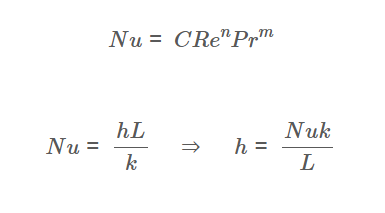1. What is a Forced Convection Correlation Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the Nusselt number (\( Nu \)) and convective heat transfer coefficient (\( h \)) for forced convection using the correlation \( Nu = C Re^n Pr^m \), which relates the Nusselt number to Reynolds and Prandtl numbers.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine \( Nu \) and \( h \) for various flow configurations, optimizing heat transfer in ducts, pipes, and heat exchangers.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following forced convection correlation:
Nusselt Number:
\[
Nu = C Re^n Pr^m
\]
Then calculates \( h \) using:
\[
Nu = \frac{h L}{k} \quad \Rightarrow \quad h = \frac{Nu k}{L}
\]
Where:
- \( Nu \): Nusselt number (dimensionless)
- \( Re \): Reynolds number (dimensionless, user input)
- \( Pr \): Prandtl number (dimensionless, user input)
- \( C, n, m \): Empirical constants (default: \( C = 0.023 \), \( n = 0.8 \), \( m = 0.4 \) for turbulent flow in pipes)
- \( h \): Convective heat transfer coefficient (Btu/hr-ft²-°F, W/m²-K)
- \( L \): Characteristic length (ft, in, m)
- \( k \): Fluid thermal conductivity (Btu-ft/hr-ft²-°F, W/m-K)
Unit Conversions:
- Characteristic Length (\( L \)): ft, in (1 in = \( \frac{1}{12} \) ft), m (1 m = 3.28084 ft)
- Thermal Conductivity (\( k \)): Btu-ft/hr-ft²-°F, W/m-K (1 W/m-K = 0.577789 Btu-ft/hr-ft²-°F)
- Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient (\( h \)): Btu/hr-ft²-°F, W/m²-K (1 Btu/hr-ft²-°F = 5.678263 W/m²-K)
Steps:
- Enter the Reynolds number (\( Re \)), Prandtl number (\( Pr \)), empirical constants (\( C \), \( n \), \( m \)), characteristic length (\( L \)), and fluid thermal conductivity (\( k \)), and select their units.
- Convert \( L \) to ft and \( k \) to Btu-ft/hr-ft²-°F.
- Calculate the Nusselt number using \( Nu = C Re^n Pr^m \).
- Calculate the convective heat transfer coefficient using \( h = \frac{Nu k}{L} \).
- Convert \( h \) to the selected unit (Btu/hr-ft²-°F, W/m²-K).
- Display both \( Nu \) and \( h \), using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Forced Convection Correlation Calculation
Calculating the Nusselt number and convective heat transfer coefficient is crucial for:
- HVAC Design: Determines heat transfer rates in ducts, pipes, and heat exchangers, optimizing system performance.
- Energy Efficiency: Helps design systems that efficiently transfer heat, reducing energy consumption.
- System Performance: Ensures accurate thermal load calculations for heating and cooling systems.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( Re = 50000 \), \( Pr = 0.7 \), \( C = 0.023 \), \( n = 0.8 \), \( m = 0.4 \), \( L = 0.5 \, \text{ft} \), \( k = 0.015 \, \text{Btu-ft/hr-ft}^2\text{-°F} \), \( h \) in Btu/hr-ft²-°F:
- Nusselt Number: \( Nu = 0.023 \times (50000)^{0.8} \times (0.7)^{0.4} \approx 40.2156 \)
- Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient: \( h = \frac{40.2156 \times 0.015}{0.5} \approx 1.2065 \, \text{Btu/hr-ft}^2\text{-°F} \)
- Example 2: For \( Re = 100000 \), \( Pr = 0.72 \), \( C = 0.023 \), \( n = 0.8 \), \( m = 0.4 \), \( L = 0.1 \, \text{m} \), \( k = 0.026 \, \text{W/m-K} \), \( h \) in W/m²-K:
- Convert: \( L = 0.1 \times 3.28084 = 0.328084 \, \text{ft} \), \( k = 0.026 \times 0.577789 = 0.0150225 \, \text{Btu-ft/hr-ft}^2\text{-°F} \)
- Nusselt Number: \( Nu = 0.023 \times (100000)^{0.8} \times (0.72)^{0.4} \approx 74.3506 \)
- Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient: \( h = \frac{74.3506 \times 0.0150225}{0.328084} \approx 3.4032 \, \text{Btu/hr-ft}^2\text{-°F} \)
- Convert to W/m²-K: \( h = 3.4032 \times 5.678263 \approx 19.3235 \, \text{W/m}^2\text{-K} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the forced convection correlation?
A: The forced convection correlation \( Nu = C Re^n Pr^m \) relates the Nusselt number to Reynolds and Prandtl numbers, used to calculate the convective heat transfer coefficient (\( h \)) in forced convection scenarios.
Q: Why is forced convection important in HVAC systems?
A: It determines heat transfer rates in ducts, pipes, and heat exchangers, ensuring efficient heating and cooling performance in HVAC systems.
Q: Where can I find the empirical constants (\( C \), \( n \), \( m \))?
A: These constants depend on flow type and geometry and are typically provided in engineering tables (e.g., Table 1-1 in the referenced pages). Common values for turbulent flow in pipes are \( C = 0.023 \), \( n = 0.8 \), \( m = 0.4 \).
Forced Convection Correlation Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back