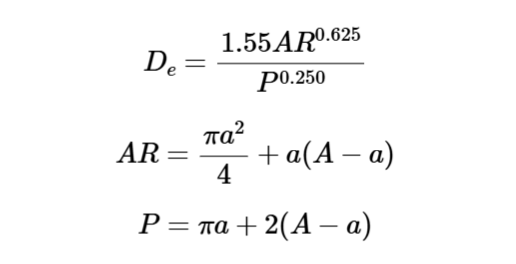1. What is a Circular Equivalent Diameter Calculator for Flat Oval Ducts?
Definition: This calculator computes the equivalent round duct diameter (\( D_e \)) for a flat oval duct with equal airflow, resistance, and length, based on its cross-sectional area and perimeter.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC design to convert flat oval duct dimensions to an equivalent circular duct diameter, simplifying pressure loss and flow calculations.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Cross-Sectional Area:
\[
A R = \frac{\pi a^2}{4} + a (A - a)
\]
Perimeter:
\[
P = \pi a + 2 (A - a)
\]
Circular Equivalent Diameter:
\[
D_e = \frac{1.55 A R^{0.625}}{P^{0.250}}
\]
Where:
- \( D_e \): Circular equivalent diameter (in., ft, m)
- \( A R \): Cross-sectional area of flat oval duct (in², ft², m²)
- \( P \): Perimeter of flat oval duct (in., ft, m)
- \( A \): Major axis of flat oval duct (in., ft, m)
- \( a \): Minor axis of flat oval duct (in., ft, m)
Unit Conversions:
- Major and Minor Axes (\( A \), \( a \)):
- in.: No conversion
- ft: 1 ft = 12 in.
- m: 1 m = 39.3701 in.
- Cross-Sectional Area (\( A R \)):
- in²: No conversion
- ft²: 1 in² = 1/144 ft²
- m²: 1 in² = 0.00064516 m²
- Perimeter (\( P \)):
- in.: No conversion
- ft: 1 in. = 1/12 ft
- m: 1 in. = 0.0254 m
- Circular Equivalent Diameter (\( D_e \)):
- in.: No conversion
- ft: 1 in. = 1/12 ft
- m: 1 in. = 0.0254 m
Steps:
- Enter the major axis (\( A \)) and minor axis (\( a \)) of the flat oval duct, and select their units.
- Convert \( A \) and \( a \) to in.
- Calculate the cross-sectional area (\( A R \)) and perimeter (\( P \)).
- Calculate the circular equivalent diameter (\( D_e \)) using the formula.
- Convert \( A R \), \( P \), and \( D_e \) to the selected units.
- Display the results with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Circular Equivalent Diameter Calculation
Calculating the circular equivalent diameter is crucial for:
- HVAC System Design: Simplifies pressure loss and flow calculations for flat oval ducts by converting them to an equivalent circular duct.
- System Efficiency: Ensures accurate resistance analysis, optimizing duct design and fan selection.
- Performance Analysis: Enables consistent calculations across different duct shapes for effective ventilation.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( A = 24 \, \text{in.} \), \( a = 12 \, \text{in.} \), results in in., in², and in.:
- \( A R = \frac{\pi \times 12^2}{4} + 12 \times (24 - 12) \approx 113.097 + 144 = 257.097 \, \text{in²} \)
- \( P = \pi \times 12 + 2 \times (24 - 12) \approx 37.699 + 24 \approx 61.699 \, \text{in.} \)
- \( D_e = \frac{1.55 \times 257.097^{0.625}}{61.699^{0.250}} \approx 20.085 \)
- Since all values are < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( A R = 257.09700 \, \text{in²} \), \( P = 61.69900 \, \text{in.} \), \( D_e = 20.08500 \, \text{in.} \)
- Example 2: For \( A = 0.6 \, \text{m} \), \( a = 0.3 \, \text{m} \), results in m, m², and m:
- Convert: \( A = 0.6 \times 39.3701 \approx 23.62206 \, \text{in.} \), \( a = 0.3 \times 39.3701 \approx 11.81103 \, \text{in.} \)
- \( A R = \frac{\pi \times 11.81103^2}{4} + 11.81103 \times (23.62206 - 11.81103) \approx 109.359 + 139.896 \approx 249.255 \, \text{in²} \)
- \( P = \pi \times 11.81103 + 2 \times (23.62206 - 11.81103) \approx 37.103 + 23.62206 \approx 60.725 \, \text{in.} \)
- \( D_e = \frac{1.55 \times 249.255^{0.625}}{60.725^{0.250}} \approx 19.684 \, \text{in.} \)
- Convert: \( A R = 249.255 \times 0.00064516 \approx 0.16083 \, \text{m²} \), \( P = 60.725 \times 0.0254 \approx 1.54242 \, \text{m} \), \( D_e = 19.684 \times 0.0254 \approx 0.49997 \, \text{m} \)
- Since all values are < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( A R = 0.16083 \, \text{m²} \), \( P = 1.54242 \, \text{m} \), \( D_e = 0.49997 \, \text{m} \)
- Example 3: For \( A = 2 \, \text{ft} \), \( a = 1 \, \text{ft} \), results in ft, ft², and ft:
- Convert: \( A = 2 \times 12 = 24 \, \text{in.} \), \( a = 1 \times 12 = 12 \, \text{in.} \)
- \( A R = \frac{\pi \times 12^2}{4} + 12 \times (24 - 12) \approx 113.097 + 144 \approx 257.097 \, \text{in²} \)
- \( P = \pi \times 12 + 2 \times (24 - 12) \approx 37.699 + 24 \approx 61.699 \, \text{in.} \)
- \( D_e = \frac{1.55 \times 257.097^{0.625}}{61.699^{0.250}} \approx 20.085 \, \text{in.} \)
- Convert: \( A R = 257.097 / 144 \approx 1.78540 \, \text{ft²} \), \( P = 61.699 / 12 \approx 5.14158 \, \text{ft} \), \( D_e = 20.085 / 12 \approx 1.67375 \, \text{ft} \)
- Since all values are < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( A R = 1.78540 \, \text{ft²} \), \( P = 5.14158 \, \text{ft} \), \( D_e = 1.67375 \, \text{ft} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does the circular equivalent diameter represent?
A: The circular equivalent diameter (\( D_e \)) is the diameter of a round duct that has the same airflow and resistance characteristics as a given flat oval duct, simplifying HVAC calculations.
Q: How can I determine the major and minor axes of a flat oval duct?
A: The major axis (\( A \)) is the longer dimension of the flat oval duct, and the minor axis (\( a \)) is the shorter dimension, measured or specified in the duct design.
Q: Why is the circular equivalent diameter important in HVAC design?
A: It allows engineers to use standard circular duct formulas for flat oval ducts, ensuring accurate pressure loss and flow calculations for system efficiency.
Circular Equivalent of Flat Oval Duct Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back