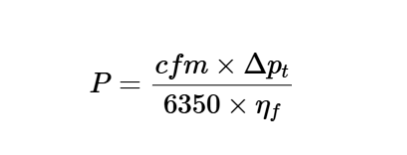1. What is a Fan Power Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the fan power (\( P \)) required to overcome the pressure drop in an HVAC system, based on air flow rate, total pressure loss, and fan efficiency.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine the energy consumption of a fan and its impact on air enthalpy, aiding in the selection and sizing of fans for efficient system operation.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for fan power:
Fan Power:
\[
P = \frac{cfm \times \Delta p_t}{6350 \times \eta_f}
\]
Where:
- \( P \): Fan power (hp, convertible to kW)
- \( cfm \): Air flow rate (ft³/min, m³/s, L/s)
- \( \Delta p_t \): Total pressure loss (inches of water, Pa, inHg)
- \( \eta_f \): Fan efficiency (dimensionless, e.g., 0.80 for 80%)
- Constant 6350: Empirical constant for converting units to horsepower (based on standard air density and unit conversions)
Unit Conversions:
- Air Flow Rate (\( cfm \)): ft³/min, m³/s (1 m³/s = 2118.88 ft³/min), L/s (1 L/s = 2.11888 ft³/min)
- Total Pressure Loss (\( \Delta p_t \)): inches of water, Pa (1 Pa = 0.00401463 inH2O), inHg (1 inHg = 13.5951 inH2O)
- Fan Power (\( P \)): hp, kW (1 hp = 0.7457 kW)
Steps:
- Enter the air flow rate (\( cfm \)), total pressure loss (\( \Delta p_t \)), and fan efficiency (\( \eta_f \)), and select their units.
- Convert air flow rate to ft³/min and total pressure loss to inches of water.
- Calculate the fan power using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (hp or kW).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Fan Power Calculation
Calculating the fan power is crucial for:
- HVAC Design: Determines the power required to operate the fan, aiding in fan selection and system design.
- Energy Efficiency: Helps optimize fan operation by selecting an efficient fan and minimizing energy consumption.
- System Performance: Ensures the fan can overcome the system pressure drop while maintaining the desired air flow, and accounts for the fan's impact on air enthalpy in psychrometric calculations.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( cfm = 13636 \, \text{ft³/min} \), \( \Delta p_t = 4 \, \text{inches of water} \), \( \eta_f = 0.80 \), fan power in hp:
- \( P = \frac{13636 \times 4}{6350 \times 0.80} \)
- \( P = \frac{54544}{5080} \approx 10.73701 \)
- Since 10.73701 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 10.73701 \)
- Example 2: For \( cfm = 2 \, \text{m³/s} \), \( \Delta p_t = 1000 \, \text{Pa} \), \( \eta_f = 0.85 \), fan power in kW:
- Convert: \( cfm = 2 \times 2118.88 = 4237.76 \, \text{ft³/min} \), \( \Delta p_t = 1000 \times 0.00401463 = 4.01463 \, \text{inches of water} \)
- \( P = \frac{4237.76 \times 4.01463}{6350 \times 0.85} \)
- \( P = \frac{17017.9925}{5397.5} \approx 3.15234 \, \text{hp} \)
- Convert to kW: \( 3.15234 \times 0.7457 = 2.35069 \)
- Since 2.35069 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 2.35069 \)
- Example 3: For \( cfm = 0.001 \, \text{ft³/min} \), \( \Delta p_t = 1 \, \text{inches of water} \), \( \eta_f = 0.90 \), fan power in hp:
- \( P = \frac{0.001 \times 1}{6350 \times 0.90} \)
- \( P = \frac{0.001}{5715} \approx 0.000000174978 \)
- Since 0.000000174978 < 0.00001, use scientific notation: \( 1.74978e-7 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is fan power in HVAC systems?
A: Fan power (\( P \)) in HVAC systems is the power required to drive a fan to overcome the pressure drop in the system, ensuring the desired air flow rate is maintained.
Q: Why is fan efficiency important in this calculation?
A: Fan efficiency (\( \eta_f \)) accounts for the energy losses in the fan, indicating how effectively the fan converts input power into air movement. Higher efficiency reduces the power required for the same air flow and pressure drop.
Q: How does fan power affect air enthalpy in HVAC systems?
A: The energy consumed by the fan is converted into heat, which increases the air enthalpy (temperature) as the air passes through the fan, impacting psychrometric calculations and system design.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back