 Home
Home
 Back
Back
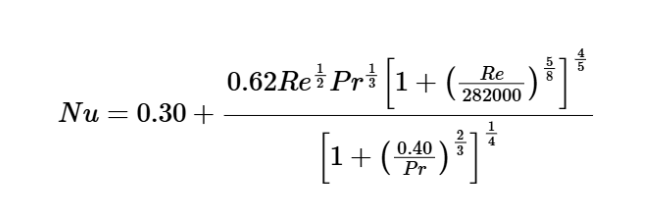
Definition: This calculator computes the average Nusselt number (\( Nu \)) for cross-flow over a circular cylinder, covering a wide range of Reynolds numbers.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine heat transfer coefficients (\( h \)) for tube bundles, such as in condensers or heat exchangers.
The calculator uses the following formula for cross-flow over a circular cylinder:
Nusselt Number: \[ Nu = 0.30 + \frac{0.62 Re^{\frac{1}{2}} Pr^{\frac{1}{3}} \left[ 1 + \left( \frac{Re}{282000} \right)^{\frac{5}{8}} \right]^{\frac{4}{5}}}{\left[ 1 + \left( \frac{0.40}{Pr} \right)^{\frac{2}{3}} \right]^{\frac{1}{4}}} \]
Where:
Steps:
Calculating the Nusselt number for cross-flow over a cylinder is crucial for:
Q: What is the cross-flow over cylinder formula?
A: It calculates the average Nusselt number for cross-flow over a circular cylinder as \( Nu = 0.30 + \frac{0.62 Re^{\frac{1}{2}} Pr^{\frac{1}{3}} \left[ 1 + \left( \frac{Re}{282000} \right)^{\frac{5}{8}} \right]^{\frac{4}{5}}}{\left[ 1 + \left( \frac{0.40}{Pr} \right)^{\frac{2}{3}} \right]^{\frac{1}{4}}} \), covering a wide range of Reynolds numbers.
Q: Why is this calculation important in HVAC systems?
A: It determines heat transfer coefficients for tube bundles in heat exchangers, such as condensers, optimizing HVAC system design.
Q: How do I determine the Reynolds number (\( Re \)) and Prandtl number (\( Pr \))?
A: \( Re \) can be calculated using a Reynolds Number Calculator with fluid properties and cylinder diameter, while \( Pr \) depends on fluid properties like viscosity, specific heat, and thermal conductivity, often available in engineering references.