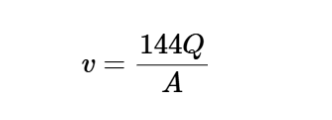1. What is an Air Velocity Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the average air velocity (\( v \)) in a duct based on the air flow rate and the cross-sectional area of the duct.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC design to determine air flow speeds in ducts, aiding in the sizing of ducts, fans, and other ventilation components for efficient system performance.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for air velocity:
Air Velocity:
\[
v = \frac{144 Q}{A}
\]
Where:
- \( v \): Fluid mean velocity (fpm, m/s)
- \( Q \): Air flow rate (cfm, m³/s)
- \( A \): Cross-sectional area of duct (in², ft², m²)
Unit Conversions:
- Air Flow Rate (\( Q \)): cfm, m³/s (1 m³/s = 2118.88 cfm)
- Cross-Sectional Area (\( A \)):
- in²: No conversion
- ft²: 1 ft² = 144 in²
- m²: 1 m² = 1550.003 in²
- Velocity (\( v \)): fpm, m/s (1 fpm = 0.00508 m/s)
Steps:
- Enter the air flow rate (\( Q \)) and cross-sectional area (\( A \)), and select their units.
- Convert \( Q \) to cfm and \( A \) to in².
- Calculate the air velocity using the formula, with the constant 144 in²/ft²-min.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (fpm or m/s).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Air Velocity Calculation
Calculating air velocity is crucial for:
- HVAC System Design: Ensures appropriate air flow speeds for efficient duct performance and fan selection.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes duct sizing to minimize pressure losses, reducing energy consumption.
- Thermal Comfort: Maintains proper air distribution for consistent indoor temperatures and ventilation.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( Q = 1000 \, \text{cfm} \), \( A = 144 \, \text{in²} \), air velocity in fpm:
- \( v = \frac{144 \times 1000}{144} = 1000 \)
- Since 1000 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 1000.00000 \)
- Example 2: For \( Q = 0.5 \, \text{m³/s} \), \( A = 0.1 \, \text{m²} \), air velocity in m/s:
- Convert: \( Q = 0.5 \times 2118.88 \approx 1059.44 \, \text{cfm} \)
- \( A = 0.1 \times 1550.003 \approx 155.0003 \, \text{in²} \)
- \( v = \frac{144 \times 1059.44}{155.0003} \approx 984.121 \, \text{fpm} \)
- Convert to m/s: \( 984.121 \times 0.00508 \approx 4.99933 \)
- Since 4.99933 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 4.99933 \)
- Example 3: For \( Q = 500 \, \text{cfm} \), \( A = 1 \, \text{ft²} \), air velocity in fpm:
- Convert: \( A = 1 \times 144 = 144 \, \text{in²} \)
- \( v = \frac{144 \times 500}{144} = 500 \)
- Since 500 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 500.00000 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does air velocity in ducts represent?
A: Air velocity (\( v \)) quantifies the speed of air flowing through a duct, critical for ensuring proper air distribution in HVAC systems.
Q: How can I determine the air flow rate and duct area?
A: Air flow rate (\( Q \)) is typically measured or specified based on system requirements. Duct area (\( A \)) is calculated from duct dimensions (e.g., circular or rectangular cross-sections).
Q: Why is air velocity important in HVAC design?
A: It affects pressure losses, noise levels, and air distribution, guiding duct and fan design for efficient and comfortable HVAC systems.
Air Velocity in Ducts Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back