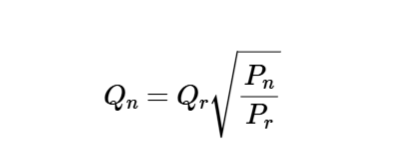1. What is an Adjusted Filter Flow Rate Based on Pressure Drop Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the new flow rate (\( Q_n \)) through a filter when the pressure drop across the filter changes, based on the rated flow rate and pressure drop.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to adjust the expected flow rate through a filter when operating conditions (pressure drop) differ from the filter's rated conditions, ensuring accurate system performance predictions.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for the adjusted filter flow rate:
Adjusted Filter Flow Rate:
\[
Q_n = Q_r \sqrt{\frac{P_n}{P_r}}
\]
Where:
- \( Q_n \): New flow rate at new pressure drop (cfm, m³/s, L/s)
- \( Q_r \): Rated flow rate at rated pressure drop (cfm, m³/s, L/s)
- \( P_n \): New pressure drop (in.wc, Pa, inHg)
- \( P_r \): Rated pressure drop (in.wc, Pa, inHg)
Unit Conversions:
- Flow Rates (\( Q_r \), \( Q_n \)): cfm, m³/s (1 m³/s = 2118.88 cfm), L/s (1 L/s = 2.11888 cfm)
- Pressure Drops (\( P_n \), \( P_r \)): in.wc, Pa (1 Pa = 0.00401865 in.wc), inHg (1 inHg = 13.6087 in.wc)
Steps:
- Enter the rated flow rate (\( Q_r \)), new pressure drop (\( P_n \)), and rated pressure drop (\( P_r \)), and select their units.
- Convert the rated flow rate to cfm and pressure drops to in.wc.
- Calculate the new flow rate using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (cfm, m³/s, or L/s).
- Display the result with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Adjusted Filter Flow Rate Calculation
Calculating the adjusted filter flow rate is crucial for:
- System Performance: Ensures accurate prediction of air flow through filters under varying pressure drops, maintaining proper ventilation and filtration.
- Energy Efficiency: Helps optimize fan operation by understanding how flow rates change with pressure, avoiding over- or under-ventilation.
- HVAC Design: Assists in selecting filters and designing systems that account for real-world operating conditions, ensuring consistent air quality and system efficiency.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( Q_r = 850 \, \text{cfm} \), \( P_n = 0.35 \, \text{in.wc} \), \( P_r = 0.20 \, \text{in.wc} \), new flow rate in cfm:
- \( Q_n = 850 \times \sqrt{\frac{0.35}{0.20}} \)
- \( Q_n = 850 \times \sqrt{1.75} \approx 850 \times 1.32288 \approx 1124.44560 \)
- Since 1124.44560 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 1124.44560 \)
- Example 2: For \( Q_r = 0.5 \, \text{m³/s} \), \( P_n = 100 \, \text{Pa} \), \( P_r = 50 \, \text{Pa} \), new flow rate in m³/s:
- Convert: \( Q_r = 0.5 \times 2118.88 = 1059.44 \, \text{cfm} \), \( P_n = 100 \times 0.00401463 = 0.401463 \, \text{in.wc} \), \( P_r = 50 \times 0.00401463 = 0.2007315 \, \text{in.wc} \)
- \( Q_n = 1059.44 \times \sqrt{\frac{0.401463}{0.2007315}} \)
- \( Q_n = 1059.44 \times \sqrt{2} \approx 1059.44 \times 1.414213562 \approx 1498.05392 \, \text{cfm} \)
- Convert to m³/s: \( 1498.05392 \times 0.000471947 \approx 0.70711 \)
- Since 0.70711 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.70711 \)
- Example 3: For \( Q_r = 1 \, \text{L/s} \), \( P_n = 0.01 \, \text{inHg} \), \( P_r = 0.02 \, \text{inHg} \), new flow rate in L/s:
- Convert: \( Q_r = 1 \times 2.11888 = 2.11888 \, \text{cfm} \), \( P_n = 0.01 \times 13.5951 = 0.135951 \, \text{in.wc} \), \( P_r = 0.02 \times 13.5951 = 0.271902 \, \text{in.wc} \)
- \( Q_n = 2.11888 \times \sqrt{\frac{0.135951}{0.271902}} \)
- \( Q_n = 2.11888 \times \sqrt{0.5} \approx 2.11888 \times 0.707106781 \approx 1.49803 \, \text{cfm} \)
- Convert to L/s: \( 1.49803 \times 0.471947 \approx 0.70711 \)
- Since 0.70711 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.70711 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why does the flow rate change with pressure drop across a filter?
A: The flow rate through a filter is proportional to the square root of the pressure drop, as described by the formula. A higher pressure drop increases the flow rate, while a lower pressure drop reduces it, due to the physics of airflow through porous media.
Q: What is the rated pressure drop of a filter?
A: The rated pressure drop (\( P_r \)) is the pressure drop across the filter at its rated flow rate (\( Q_r \)), as specified by the manufacturer, typically under standard test conditions.
Q: How can I determine the new pressure drop for my system?
A: The new pressure drop (\( P_n \)) can be measured using a manometer or pressure sensor across the filter during operation, or estimated based on changes in system conditions (e.g., fan speed, filter condition).
Adjusted Filter Flow Rate Based on Pressure Drop Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back