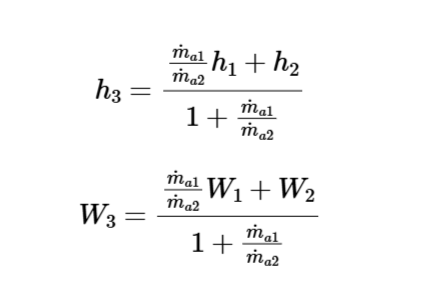1. What is an Adiabatic Mixing of Two Air Streams Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the enthalpy (\( h_3 \)) and humidity ratio (\( W_3 \)) of the mixed air resulting from the adiabatic mixing of two air streams with different psychrometric properties.
Purpose: It is used in HVAC systems to determine the properties of mixed air in ventilation systems, aiding in the design and analysis of air mixing processes for temperature and humidity control.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas for the mixed air properties:
Mixed Air Enthalpy:
\[
h_3 = \frac{\frac{\dot{m}_{a1}}{\dot{m}_{a2}} h_1 + h_2}{1 + \frac{\dot{m}_{a1}}{\dot{m}_{a2}}}
\]
Mixed Air Humidity Ratio:
\[
W_3 = \frac{\frac{\dot{m}_{a1}}{\dot{m}_{a2}} W_1 + W_2}{1 + \frac{\dot{m}_{a1}}{\dot{m}_{a2}}}
\]
Where:
- \( h_3 \): Enthalpy of mixed air (Btu/lb_m, convertible to kJ/kg)
- \( W_3 \): Humidity ratio of mixed air (lb_v/lb_da, kg_v/kg_da)
- \( \dot{m}_{a1} \): Mass flow rate of air stream 1 (lb_m/hr, kg/hr)
- \( \dot{m}_{a2} \): Mass flow rate of air stream 2 (lb_m/hr, kg/hr)
- \( h_1 \): Enthalpy of air stream 1 (Btu/lb_m, kJ/kg)
- \( h_2 \): Enthalpy of air stream 2 (Btu/lb_m, kJ/kg)
- \( W_1 \): Humidity ratio of air stream 1 (lb_v/lb_da, kg_v/kg_da)
- \( W_2 \): Humidity ratio of air stream 2 (lb_v/lb_da, kg_v/kg_da)
Unit Conversions:
- Mass Flow Rates (\( \dot{m}_{a1} \), \( \dot{m}_{a2} \)): lb_m/hr, kg/hr (1 kg/hr = 2.20462 lb_m/hr)
- Enthalpies (\( h_1 \), \( h_2 \), \( h_3 \)): Btu/lb_m, kJ/kg (1 kJ/kg = 0.429923 Btu/lb_m, 1 Btu/lb_m = 2.326 kJ/kg)
- Humidity Ratios (\( W_1 \), \( W_2 \), \( W_3 \)): lb_v/lb_da, kg_v/kg_da (numerically the same, label changes for clarity)
Steps:
- Enter the mass flow rates (\( \dot{m}_{a1} \), \( \dot{m}_{a2} \)), enthalpies (\( h_1 \), \( h_2 \)), and humidity ratios (\( W_1 \), \( W_2 \)) of the two air streams, and select their units.
- Convert mass flow rates to lb_m/hr, enthalpies to Btu/lb_m, and ensure humidity ratios are consistent.
- Calculate the mass flow ratio (\( \frac{\dot{m}_{a1}}{\dot{m}_{a2}} \)).
- Calculate the mixed air enthalpy (\( h_3 \)) and humidity ratio (\( W_3 \)) using the formulas.
- Convert the results to the selected units (Btu/lb_m or kJ/kg for \( h_3 \); lb_v/lb_da or kg_v/kg_da for \( W_3 \)).
- Display the results with 5 decimal places, or in scientific notation if the value is greater than 10,000 or less than 0.00001.
3. Importance of Adiabatic Mixing Calculation
Calculating the properties of mixed air in an adiabatic mixing process is crucial for:
- HVAC Design: Determines the resulting temperature and humidity of mixed air, aiding in the design of ventilation systems and air handling units.
- Energy Efficiency: Helps optimize mixing processes by predicting the psychrometric state of the mixed air, ensuring efficient temperature and humidity control.
- System Performance: Ensures the system can achieve the desired conditions for comfort or process requirements by accurately predicting mixed air properties.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( \dot{m}_{a1} = 6410 \, \text{lb_m/hr} \), \( \dot{m}_{a2} = 19708 \, \text{lb_m/hr} \), \( h_1 = 31.54 \, \text{Btu/lb_m} \), \( h_2 = 30.20 \, \text{Btu/lb_m} \), \( W_1 = 0.009 \, \text{lb_v/lb_da} \), \( W_2 = 0.0111 \, \text{lb_v/lb_da} \):
- Ratio: \( \frac{\dot{m}_{a1}}{\dot{m}_{a2}} = \frac{6410}{19708} \approx 0.325249 \)
- \( h_3 = \frac{0.325249 \times 31.54 + 30.20}{1 + 0.325249} \)
- \( h_3 = \frac{10.258349 + 30.20}{1.325249} \approx \frac{40.458349}{1.325249} \approx 30.52354 \, \text{Btu/lb_m} \)
- Since 30.52354 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 30.52354 \)
- \( W_3 = \frac{0.325249 \times 0.009 + 0.0111}{1 + 0.325249} \)
- \( W_3 = \frac{0.002927241 + 0.0111}{1.325249} \approx \frac{0.014027241}{1.325249} \approx 0.010582 \)
- Since 0.010582 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.01058 \)
- Example 2: For \( \dot{m}_{a1} = 1000 \, \text{kg/hr} \), \( \dot{m}_{a2} = 2000 \, \text{kg/hr} \), \( h_1 = 50 \, \text{kJ/kg} \), \( h_2 = 70 \, \text{kJ/kg} \), \( W_1 = 0.008 \, \text{kg_v/kg_da} \), \( W_2 = 0.012 \, \text{kg_v/kg_da} \), results in kJ/kg and kg_v/kg_da:
- Convert: \( \dot{m}_{a1} = 1000 \times 2.20462 = 2204.62 \, \text{lb_m/hr} \), \( \dot{m}_{a2} = 2000 \times 2.20462 = 4409.24 \, \text{lb_m/hr} \), \( h_1 = 50 \times 0.429923 = 21.4962 \, \text{Btu/lb_m} \), \( h_2 = 70 \times 0.429923 = 30.0946 \, \text{Btu/lb_m} \)
- Ratio: \( \frac{\dot{m}_{a1}}{\dot{m}_{a2}} = \frac{2204.62}{4409.24} = 0.5 \)
- \( h_3 = \frac{0.5 \times 21.4962 + 30.0946}{1 + 0.5} \)
- \( h_3 = \frac{10.7481 + 30.0946}{1.5} \approx \frac{40.8427}{1.5} \approx 27.22847 \, \text{Btu/lb_m} \)
- Convert to kJ/kg: \( 27.22847 \times 2.326 = 63.33342 \)
- Since 63.33342 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 63.33342 \)
- \( W_3 = \frac{0.5 \times 0.008 + 0.012}{1 + 0.5} \)
- \( W_3 = \frac{0.004 + 0.012}{1.5} = \frac{0.016}{1.5} \approx 0.01066667 \)
- Since 0.01066667 < 10000 and > 0.00001, display with 5 decimal places: \( 0.01067 \)
- Example 3: For \( \dot{m}_{a1} = 0.01 \, \text{lb_m/hr} \), \( \dot{m}_{a2} = 0.02 \, \text{lb_m/hr} \), \( h_1 = 0.00002 \, \text{Btu/lb_m} \), \( h_2 = 0.00003 \, \text{Btu/lb_m} \), \( W_1 = 0.0000001 \, \text{lb_v/lb_da} \), \( W_2 = 0.0000002 \, \text{lb_v/lb_da} \), results in Btu/lb_m and lb_v/lb_da:
- Ratio: \( \frac{\dot{m}_{a1}}{\dot{m}_{a2}} = \frac{0.01}{0.02} = 0.5 \)
- \( h_3 = \frac{0.5 \times 0.00002 + 0.00003}{1 + 0.5} \)
- \( h_3 = \frac{0.00001 + 0.00003}{1.5} = \frac{0.00004}{1.5} \approx 0.0000266667 \)
- Since 0.0000266667 < 0.00001, use scientific notation: \( 2.66667e-5 \)
- \( W_3 = \frac{0.5 \times 0.0000001 + 0.0000002}{1 + 0.5} \)
- \( W_3 = \frac{0.00000005 + 0.0000002}{1.5} = \frac{0.00000025}{1.5} \approx 0.000000166667 \)
- Since 0.000000166667 < 0.00001, use scientific notation: \( 1.66667e-7 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is adiabatic mixing in HVAC systems?
A: Adiabatic mixing in HVAC systems involves combining two air streams without external heat exchange, where the resulting air properties (enthalpy and humidity) are a weighted average of the two streams based on their mass flow rates.
Q: Why are psychrometric charts needed for this calculation?
A: Psychrometric charts provide the enthalpy (\( h_1 \), \( h_2 \)) and humidity ratio (\( W_1 \), \( W_2 \)) of each air stream, which are necessary inputs for calculating the mixed air properties.
Q: How do I determine the enthalpy and humidity ratio values if I don’t have a psychrometric chart?
A: Enthalpy and humidity ratios can be calculated using psychrometric equations or software, based on temperature, pressure, and humidity conditions of each air stream, or approximated using standard air properties.
Adiabatic Mixing of Two Air Streams Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back