 Home
Home
 Back
Back
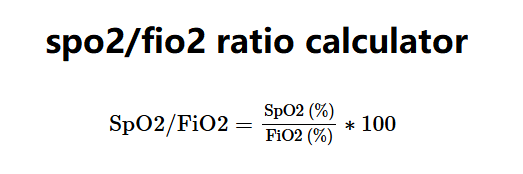
The SpO2/FiO2 Ratio Calculator computes the ratio of peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) to the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) as a noninvasive surrogate for assessing lung function, especially in acute respiratory failure. The formula is:
Where:
Enter the SpO2 and FiO2 values, and calculate the result.
Note: FiO2 is entered as a percentage and converted to a decimal for calculation.
This calculator is useful for clinicians assessing hypoxemia in patients with acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) when arterial blood gas is unavailable.
Input the SpO2 (%) and FiO2 (%). The calculator outputs the ratio.
Example 1: For SpO2 of 95% and FiO2 of 40%.
Example 2: For SpO2 of 98% and FiO2 of 21%.
Use this tool for quick assessments in critical care settings.
Below are frequently asked questions about SpO2/FiO2 Ratio:
Interpreting results for adults (Rice, 2007):
For use in ARDS:
S/F Ratio Thresholds for Specific ARDS Categories (per the "global definition" of ARDS)
| Category | S/F Ratio Criteria* |
|---|---|
| Nonintubated ARDS | ≤315 on HFNC with flow of ≥30 L/min or NIV/CPAP with ≥5 cm H₂O end-expiratory pressure |
| Intubated ARDS | Mild: >235 and ≤315 |
| Moderate: >148 and ≤235 | |
| Severe: ≤148 | |
| Modified definition for resource-limited settings | ≤315** |
*If SpO₂ ≤97%
**Neither positive end-expiratory pressure nor a minimum flow rate of oxygen is required for diagnosis in resource-limited settings.
Keep in mind that the S/F ratio is just one of several criteria used in the diagnosis and severity classification of ARDS.