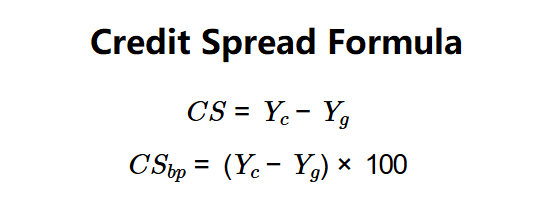1. What is the Credit Spread Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the credit spread (\( CS \)), the difference in yield between a corporate bond and a government bond, reflecting the additional risk premium for the corporate bond.
Purpose: Helps investors evaluate the extra yield demanded for holding a corporate bond over a risk-free government bond, aiding in risk assessment.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses two formulas to compute the credit spread:
Formulas:
\( CS = Y_c - Y_g \)
\( CS_{bp} = (Y_c - Y_g) \times 100 \)
Where:
- \( CS \): Credit Spread (%)
- \( CS_{bp} \): Credit Spread (basis points)
- \( Y_c \): Corporate Bond Yield (%)
- \( Y_g \): Government Bond Yield (%)
Steps:
- Step 1: Input corporate bond yield. Provide \( Y_c \).
- Step 2: Input government bond yield. Provide \( Y_g \).
- Step 3: Calculate credit spread. Compute \( CS = Y_c - Y_g \) and convert to basis points.
3. Importance of Credit Spread Calculation
Calculating the credit spread is crucial for:
- Risk Assessment: Indicates the additional risk of a corporate bond compared to a government bond, per.
- Investment Decisions: Helps investors decide if the risk premium justifies holding the corporate bond.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: \( Y_c = 5.3\% \), \( Y_g = 1.8\% \):
- Step 1: \( Y_c = 5.3\% \).
- Step 2: \( Y_g = 1.8\% \).
- Step 3:
- \( CS = 5.3 - 1.8 = 3.50\% \).
- \( CS_{bp} = 3.50 \times 100 = 350 \).
- Results: \( Y_c = 5.30\% \), \( Y_g = 1.80\% \), \( CS = 3.50\% \), \( CS_{bp} = 350 \).
A credit spread of 3.50% (350 basis points) reflects the risk premium for the corporate bond.
Example 2: \( Y_c = 6.5\% \), \( Y_g = 2.0\% \):
- Step 1: \( Y_c = 6.5\% \).
- Step 2: \( Y_g = 2.0\% \).
- Step 3:
- \( CS = 6.5 - 2.0 = 4.50\% \).
- \( CS_{bp} = 4.50 \times 100 = 450 \).
- Results: \( Y_c = 6.50\% \), \( Y_g = 2.00\% \), \( CS = 4.50\% \), \( CS_{bp} = 450 \).
A higher spread of 4.50% indicates greater perceived risk.
Example 3: \( Y_c = 4.0\% \), \( Y_g = 3.0\% \):
- Step 1: \( Y_c = 4.0\% \).
- Step 2: \( Y_g = 3.0\% \).
- Step 3:
- \( CS = 4.0 - 3.0 = 1.00\% \).
- \( CS_{bp} = 1.00 \times 100 = 100 \).
- Results: \( Y_c = 4.00\% \), \( Y_g = 3.00\% \), \( CS = 1.00\% \), \( CS_{bp} = 100 \).
A narrow spread of 1.00% suggests lower risk.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is credit spread important?
A: It measures the risk premium investors demand for a corporate bond over a risk-free government bond, per Investopedia.
Q: Can credit spread be negative?
A: Rare, but possible if a corporate bond yields less than a government bond, indicating lower perceived risk, which is uncommon.
Simple Credit Spread Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back