 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the Retention Ratio, a financial metric that measures the percentage of net income a company retains after paying dividends to common shareholders, reflecting the portion of earnings reinvested in the business.
Purpose: Helps investors and analysts evaluate a company’s dividend policy and growth potential, as a higher retention ratio indicates more funds available for reinvestment, while a lower ratio suggests a focus on dividend payouts.
The calculator follows a two-step process to compute the retention ratio:
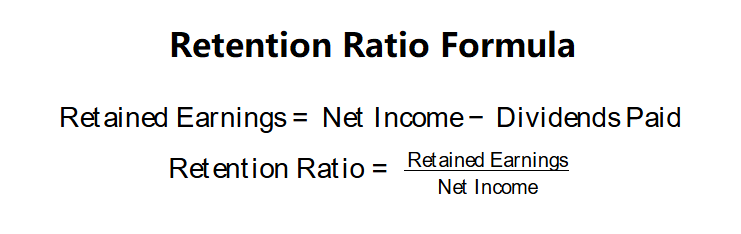
Retention Ratio Formulas:
Steps:
Calculating the retention ratio is crucial for:
Example (Company Alpha): Net Income = $1,000,000, Dividends Paid = $350,000:
A retention ratio of 65% indicates Company Alpha reinvests 65% of its earnings, balancing growth and dividend payouts.
Example 2: Net Income = $2,000,000, Dividends Paid = $800,000:
A retention ratio of 60% suggests the company retains a significant portion of earnings for reinvestment.
Example 3: Net Income = $500,000, Dividends Paid = $400,000:
A retention ratio of 20% indicates a strong focus on dividend payouts, with limited reinvestment.
Q: What is a good retention ratio?
A: A retention ratio between 50% and 75% is often considered balanced, supporting both growth and dividends, but it depends on the company’s strategy and industry. Growth firms may have higher ratios, while mature firms favor lower ratios.
Q: Can the retention ratio be negative?
A: Yes, if dividends exceed net income, but this is unsustainable and may indicate financial distress or reliance on reserves or debt.
Q: How does the retention ratio affect stock valuation?
A: A higher retention ratio can signal future growth potential, increasing stock value if reinvestments are effective, while a lower ratio may appeal to income investors but limit growth prospects.