 Home
Home
 Back
Back
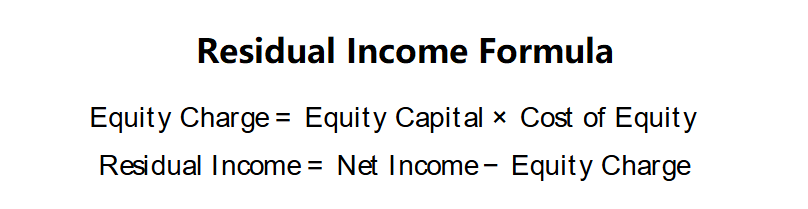
Definition: This calculator computes the Residual Income, a financial metric that measures a company’s economic profit by subtracting the cost of equity (equity charge) from its net income, reflecting the true return to shareholders after accounting for the opportunity cost of capital.
Purpose: Helps investors and managers assess whether a company generates returns above its cost of equity, useful for valuation, performance evaluation, and investment decisions, especially for firms with positive accounting profits but potential economic losses.
The calculator follows a three-step process to compute the residual income:
Residual Income Formulas:
Steps:
Calculating residual income is crucial for:
Example (Company Alpha): Net Income = $80,520,000, Equity Capital = $800,000,000, Cost of Equity = 12.3%:
A negative residual income of -$17,880,000 indicates Company Alpha is economically unprofitable, despite positive net income, as it fails to cover the cost of equity.
Example 2: Net Income = $120,000,000, Equity Capital = $500,000,000, Cost of Equity = 10%:
A positive residual income of $70,000,000 suggests the company is generating economic profit, exceeding its cost of equity.
Example 3: Net Income = $50,000,000, Equity Capital = $600,000,000, Cost of Equity = 15%:
A negative residual income of -$40,000,000 indicates the company is not covering its equity cost, signaling economic unprofitability.
Q: What does a negative residual income mean?
A: A negative residual income indicates the company is not generating enough profit to cover the cost of equity, suggesting economic unprofitability despite positive accounting profits.
Q: How is the cost of equity calculated?
A: The cost of equity is often calculated using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which considers the risk-free rate, market return, and the company’s beta. Other methods include the dividend discount model.
Q: Why is residual income better than net income for valuation?
A: Residual income accounts for the cost of equity, reflecting the true economic profit available to shareholders, whereas net income only considers debt costs, potentially overstating profitability