 Home
Home
 Back
Back
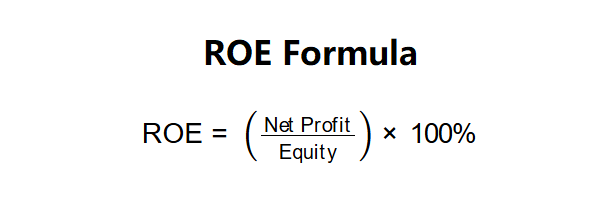
Definition: This calculator computes the Return on Equity (ROE), a financial metric that measures a company’s profitability by calculating how much net profit is generated per dollar of shareholders’ equity.
Purpose: Helps investors and analysts evaluate a company’s efficiency in using equity to generate profits, facilitating comparisons across companies or industries to assess financial performance and investment potential.
The calculator follows a two-step process to compute the ROE:
ROE Formula:
Steps:
Calculating the ROE is crucial for:
Example: Net Profit = $10,000,000, Equity = $50,000,000:
An ROE of 20% suggests the company generates $0.20 in profit per dollar of equity, indicating strong profitability if above industry averages.
Example 2: Net Profit = $5,000,000, Equity = $100,000,000:
An ROE of 5% is low, potentially indicating inefficiency or underperformance compared to industry peers.
Example 3: Net Profit = $15,000,000, Equity = $75,000,000:
An ROE of 20% is robust, suggesting effective use of equity, but should be compared to industry norms.
Q: What is a good ROE?
A: An ROE of 15–20% is generally considered good, but it varies by industry. Compare to industry averages; higher ROE is better, but excessive ROE may indicate high debt levels.
Q: Can ROE be negative?
A: Yes, if net profit is negative (losses) or equity is negative (liabilities exceed assets), indicating poor financial performance or distress.
Q: Why is industry comparison important for ROE?
A: ROE varies by industry due to differences in capital structure and profitability. For example, tech firms may have higher ROE than utilities, so context is critical for interpretation.