 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the Return on Assets (ROA), a financial metric that measures a company’s profitability by calculating how much net profit is generated per dollar of total assets.
Purpose: Helps investors and analysts evaluate a company’s efficiency in using its assets to generate profits, facilitating comparisons across companies or industries to assess financial performance.
The calculator follows a two-step process to compute the ROA:
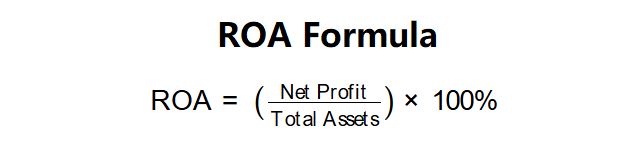
ROA Formula:
Steps:
Calculating the ROA is crucial for:
Example A: Net Profit = $10,580, Total Assets = $8,800:
An ROA of 120.23% is exceptionally high, suggesting excellent asset efficiency, but may indicate unusual circumstances (e.g., low asset base) and requires industry comparison.
Example B: Net Profit = $32,550, Total Assets = $3,100:
An ROA of 1050% is extraordinarily high, likely due to a very low asset base, and warrants scrutiny for sustainability and industry context.
Example C: Net Profit = $5,000,000, Total Assets = $25,000,000:
An ROA of 20% is strong, indicating efficient asset use, especially if above industry averages.
Q: What is a good ROA?
A: An ROA of 5–10% is typically considered good, but it varies by industry. Higher ROA is better, but extremely high values (e.g., >100%) may indicate anomalies like low asset bases or high leverage.
Q: Can ROA be negative?
A: Yes, if net profit is negative (due to losses), indicating the company is not generating profit from its assets, signaling financial challenges.
Q: Why is industry comparison important for ROA?
A: ROA varies by industry due to differences in asset intensity. For example, asset-heavy industries like manufacturing have lower ROA than asset-light sectors like software, so context is critical.