1. What is the PEG Ratio Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the Price/Earnings to Growth (PEG) Ratio, a valuation metric that adjusts the P/E ratio for the company’s expected earnings growth rate.
Purpose: Helps investors assess whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued by considering both its earnings and growth potential, aiding in investment decisions.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator follows a five-step process to compute the PEG ratio:
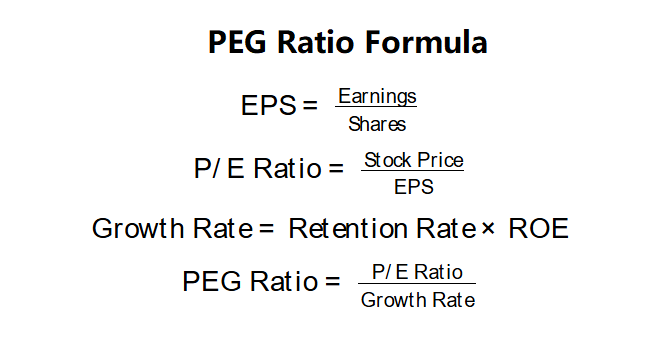
PEG Ratio Formulas:
\( \text{EPS} = \frac{\text{Earnings}}{\text{Shares}} \)
\( \text{P/E Ratio} = \frac{\text{Stock Price}}{\text{EPS}} \)
\( \text{Growth Rate} = \text{Retention Rate} \times \text{ROE} \)
\( \text{PEG Ratio} = \frac{\text{P/E Ratio}}{\text{Growth Rate}} \)
Where:
- \( \text{Earnings} \): Latest annual earnings (dollars)
- \( \text{Shares} \): Number of shares outstanding (shares)
- \( \text{Stock Price} \): Current price per share (dollars/share)
- \( \text{Retention Rate} \): Percentage of earnings retained (decimal)
- \( \text{ROE} \): Return on Equity (decimal)
- \( \text{Growth Rate} \): Earnings growth rate (percentage)
Note: The growth rate is expressed as a percentage, so the PEG ratio divides the P/E ratio by the growth rate in percentage terms.
Steps:
- Step 1: Determine the stock price. Obtain the current market price per share from financial websites.
- Step 2: Compute the EPS. Divide the company’s latest earnings by the number of shares outstanding.
- Step 3: Calculate the P/E ratio. Divide the stock price by the EPS.
- Step 4: Calculate the earnings growth rate. Multiply the retention rate by the ROE.
- Step 5: Compute the PEG ratio. Divide the P/E ratio by the growth rate (in percentage).
3. Importance of PEG Ratio
Calculating the PEG ratio is crucial for:
- Valuation Analysis: Balances a stock’s price with its growth potential, offering a more nuanced view than the P/E ratio alone.
- Investment Decisions: Helps identify undervalued stocks (low PEG) or overvalued stocks (high PEG) within an industry.
- Comparative Analysis: Allows comparison of companies with different growth rates and P/E ratios.
4. Using the Calculator
Example (Company Alpha): Stock Price = $20.00, Earnings = $15,000,000, Shares = 10,000,000, Retention Rate = 60%, ROE = 8%:
- Step 1: Stock Price: $20.00
- Step 2: EPS: \( \frac{15,000,000}{10,000,000} = 1.50 \) dollars/share
- Step 3: P/E Ratio: \( \frac{20.00}{1.50} = 13.33 \) times
- Step 4: Growth Rate: \( 0.60 \times 0.08 = 0.048 \) or 4.80%
- Step 5: PEG Ratio: \( \frac{13.33}{4.80} = 2.778 \) times
- Result: EPS = $1.50, P/E Ratio = 13.33, Growth Rate = 4.80%, PEG Ratio = 2.778 times
A PEG ratio of 2.778 suggests Company Alpha may be overvalued, as it exceeds the typical benchmark of 1.
Example 2: Stock Price = $50.00, Earnings = $20,000,000, Shares = 5,000,000, Retention Rate = 50%, ROE = 10%:
- Step 1: Stock Price: $50.00
- Step 2: EPS: \( \frac{20,000,000}{5,000,000} = 4.00 \) dollars/share
- Step 3: P/E Ratio: \( \frac{50.00}{4.00} = 12.50 \) times
- Step 4: Growth Rate: \( 0.50 \times 0.10 = 0.05 \) or 5.00%
- Step 5: PEG Ratio: \( \frac{12.50}{5.00} = 2.500 \) times
- Result: EPS = $4.00, P/E Ratio = 12.50, Growth Rate = 5.00%, PEG Ratio = 2.500 times
A PEG ratio of 2.500 indicates potential overvaluation.
Example 3: Stock Price = $30.00, Earnings = $12,000,000, Shares = 8,000,000, Retention Rate = 70%, ROE = 12%:
- Step 1: Stock Price: $30.00
- Step 2: EPS: \( \frac{12,000,000}{8,000,000} = 1.50 \) dollars/share
- Step 3: P/E Ratio: \( \frac{30.00}{1.50} = 20.00 \) times
- Step 4: Growth Rate: \( 0.70 \times 0.12 = 0.084 \) or 8.40%
- Step 5: PEG Ratio: \( \frac{20.00}{8.40} = 2.381 \) times
- Result: EPS = $1.50, P/E Ratio = 20.00, Growth Rate = 8.40%, PEG Ratio = 2.381 times
A PEG ratio of 2.381 suggests the stock may be overvalued compared to its growth.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a good PEG ratio?
A: A PEG ratio around 1 is often considered fair value, indicating the stock’s price aligns with its growth. Below 1 suggests undervaluation, while above 1 (e.g., >2) may indicate overvaluation, though industry norms vary.
Q: How does retention rate affect the PEG ratio?
A: A higher retention rate increases the earnings growth rate, potentially lowering the PEG ratio and making the stock appear more attractive.
Q: Can the PEG ratio be negative?
A: Yes, if earnings or growth rate are negative, but such cases are less meaningful for valuation and may indicate financial issues.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back