1. What is the Price to Book (P/B) Ratio Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the Price to Book (P/B) Ratio and Price to Tangible Book (P/TB) Ratio, financial metrics that compare a company’s market share price to its book value per share, indicating whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued relative to its net assets.
Purpose: Helps investors assess a company’s valuation, particularly for asset-heavy industries like banking, and identify potential investment opportunities by comparing market price to accounting value.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator follows a step-by-step process to compute the P/B and P/TB ratios:
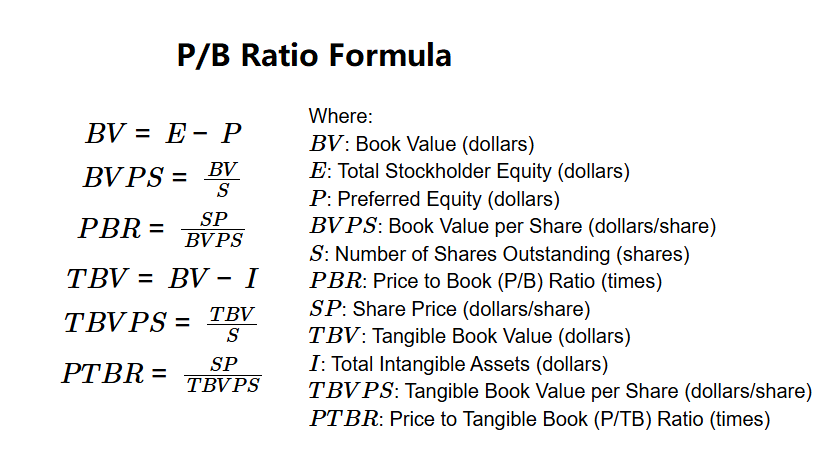
P/B and P/TB Ratio Formulas:
\( BV = E - P \)
\( BVPS = \frac{BV}{S} \)
\( PBR = \frac{SP}{BVPS} \)
\( TBV = BV - I \)
\( TBVPS = \frac{TBV}{S} \)
\( PTBR = \frac{SP}{TBVPS} \)
Where:
- \( BV \): Book Value (dollars)
- \( E \): Total Stockholder Equity (dollars)
- \( P \): Preferred Equity (dollars)
- \( BVPS \): Book Value per Share (dollars/share)
- \( S \): Number of Shares Outstanding (shares)
- \( PBR \): Price to Book (P/B) Ratio (times)
- \( SP \): Share Price (dollars/share)
- \( TBV \): Tangible Book Value (dollars)
- \( I \): Total Intangible Assets (dollars)
- \( TBVPS \): Tangible Book Value per Share (dollars/share)
- \( PTBR \): Price to Tangible Book (P/TB) Ratio (times)
Steps:
- Step 1: Calculate Book Value (\( BV \)). Subtract Preferred Equity (\( P \)) from Total Stockholder Equity (\( E \)).
- Step 2: Calculate Book Value per Share (\( BVPS \)). Divide Book Value (\( BV \)) by Number of Shares Outstanding (\( S \)).
- Step 3: Calculate P/B Ratio (\( PBR \)). Divide Share Price (\( SP \)) by Book Value per Share (\( BVPS \)).
- Step 4: Calculate Tangible Book Value (\( TBV \)). Subtract Total Intangible Assets (\( I \)) from Book Value (\( BV \)).
- Step 5: Calculate Tangible Book Value per Share (\( TBVPS \)). Divide Tangible Book Value (\( TBV \)) by Number of Shares Outstanding (\( S \)).
- Step 6: Calculate P/TB Ratio (\( PTBR \)). Divide Share Price (\( SP \)) by Tangible Book Value per Share (\( TBVPS \)).
3. Importance of P/B and P/TB Ratios
Calculating these ratios is crucial for:
- Valuation Analysis: A low P/B or P/TB ratio may indicate undervaluation, while a high ratio suggests overvaluation or strong market confidence in future growth.
- Industry Relevance: Particularly useful for asset-intensive sectors (e.g., banking, real estate) where book value reflects tangible worth.
- Financial Health: P/TB ratio excludes intangibles, providing a conservative view of a company’s net asset value.
4. Using the Calculator
Example: \( SP = \$20.00 \), \( E = \$50,000,000 \), \( P = \$5,000,000 \), \( I = \$10,000,000 \), \( S = 2,000,000 \):
- Step 1: Book Value: \( BV = 50,000,000 - 5,000,000 = 45,000,000 \) dollars
- Step 2: Book Value per Share: \( BVPS = \frac{45,000,000}{2,000,000} = 22.50 \) dollars/share
- Step 3: P/B Ratio: \( PBR = \frac{20.00}{22.50} = 0.89 \) times
- Step 4: Tangible Book Value: \( TBV = 45,000,000 - 10,000,000 = 35,000,000 \) dollars
- Step 5: Tangible Book Value per Share: \( TBVPS = \frac{35,000,000}{2,000,000} = 17.50 \) dollars/share
- Step 6: P/TB Ratio: \( PTBR = \frac{20.00}{17.50} = 1.14 \) times
- Result: \( BV = \$45,000,000.00 \), \( BVPS = \$22.50 \), \( PBR = 0.89 \) times, \( TBV = \$35,000,000.00 \), \( TBVPS = \$17.50 \), \( PTBR = 1.14 \) times
A \( PBR \) of 0.89 suggests potential undervaluation, while a \( PTBR \) of 1.14 is closer to fair value, depending on industry norms.
Example 2: \( SP = \$30.00 \), \( E = \$100,000,000 \), \( P = \$0 \), \( I = \$20,000,000 \), \( S = 5,000,000 \):
- Step 1: Book Value: \( BV = 100,000,000 - 0 = 100,000,000 \) dollars
- Step 2: Book Value per Share: \( BVPS = \frac{100,000,000}{5,000,000} = 20.00 \) dollars/share
- Step 3: P/B Ratio: \( PBR = \frac{30.00}{20.00} = 1.50 \) times
- Step 4: Tangible Book Value: \( TBV = 100,000,000 - 20,000,000 = 80,000,000 \) dollars
- Step 5: Tangible Book Value per Share: \( TBVPS = \frac{80,000,000}{5,000,000} = 16.00 \) dollars/share
- Step 6: P/TB Ratio: \( PTBR = \frac{30.00}{16.00} = 1.88 \) times
- Result: \( BV = \$100,000,000.00 \), \( BVPS = \$20.00 \), \( PBR = 1.50 \) times, \( TBV = \$80,000,000.00 \), \( TBVPS = \$16.00 \), \( PTBR = 1.88 \) times
A \( PBR \) of 1.50 and \( PTBR \) of 1.88 suggest the stock may be fairly valued or slightly overvalued, depending on the sector.
Example 3: \( SP = \$10.00 \), \( E = \$25,000,000 \), \( P = \$2,000,000 \), \( I = \$3,000,000 \), \( S = 1,000,000 \):
- Step 1: Book Value: \( BV = 25,000,000 - 2,000,000 = 23,000,000 \) dollars
- Step 2: Book Value per Share: \( BVPS = \frac{23,000,000}{1,000,000} = 23.00 \) dollars/share
- Step 3: P/B Ratio: \( PBR = \frac{10.00}{23.00} = 0.43 \) times
- Step 4: Tangible Book Value: \( TBV = 23,000,000 - 3,000,000 = 20,000,000 \) dollars
- Step 5: Tangible Book Value per Share: \( TBVPS = \frac{20,000,000}{1,000,000} = 20.00 \) dollars/share
- Step 6: P/TB Ratio: \( PTBR = \frac{10.00}{20.00} = 0.50 \) times
- Result: \( BV = \$23,000,000.00 \), \( BVPS = \$23.00 \), \( PBR = 0.43 \) times, \( TBV = \$20,000,000.00 \), \( TBVPS = \$20.00 \), \( PTBR = 0.50 \) times
Low \( PBR \) (0.43) and \( PTBR \) (0.50) ratios strongly suggest undervaluation, potentially indicating a bargain or underlying financial concerns.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a good P/B ratio?
A: A \( PBR \) below 1 may indicate undervaluation, while above 3 may suggest overvaluation, but it depends on the industry. For example, banks often have \( PBR \) around 1–2, while tech firms may have higher ratios. Compare to industry peers for context.
Q: Why is the P/TB ratio important?
A: The \( PTBR \) excludes intangible assets (e.g., goodwill), providing a more conservative valuation, especially for companies with significant intangibles or in distressed situations.
Q: Can the P/B ratio be negative?
A: Yes, if \( BV \) is negative (liabilities exceed assets), but this is rare and signals financial distress. Negative ratios are less meaningful for valuation.
Price to Book (P/B) Ratio Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back