 Home
Home
 Back
Back
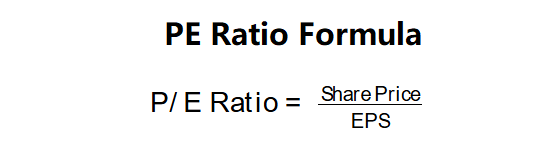
Definition: This calculator computes the Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio, a financial metric that measures a company’s share price relative to its earnings per share (EPS), indicating how much investors pay per dollar of earnings.
Purpose: Helps investors evaluate whether a stock is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly valued, facilitating comparisons within the same industry for investment decisions.
The calculator uses the following formula to compute the P/E ratio:
P/E Ratio Formula:
Steps:
Calculating the P/E ratio is crucial for:
Example: Share Price = $25.00, EPS = $1.80:
A P/E ratio of 13.89 suggests the stock is fairly valued if aligned with industry averages (e.g., 10–20), but it may be undervalued if competitors have higher ratios.
Example 2: Share Price = $50.00, EPS = $2.50:
A P/E ratio of 20.00 may indicate high growth expectations or potential overvaluation, depending on the industry context.
Example 3: Share Price = $15.00, EPS = $2.00:
A P/E ratio of 7.50 suggests the stock may be undervalued or facing lower growth expectations compared to its peers.
Q: What is a good P/E ratio?
A: A P/E ratio between 10 and 20 is often considered reasonable, but it varies by industry. Compare the P/E to industry averages; lower ratios may indicate undervaluation, higher ones overvaluation or growth expectations.
Q: What does a negative P/E ratio mean?
A: A negative P/E ratio occurs when EPS is negative (due to losses), making the ratio non-meaningful for valuation. It suggests financial challenges and requires further analysis.
Q: Why is the P/E ratio industry-specific?
A: Different industries have varying growth rates and risk profiles, affecting P/E norms. For example, tech companies often have higher P/E ratios than utilities due to higher growth expectations.