 Home
Home
 Back
Back
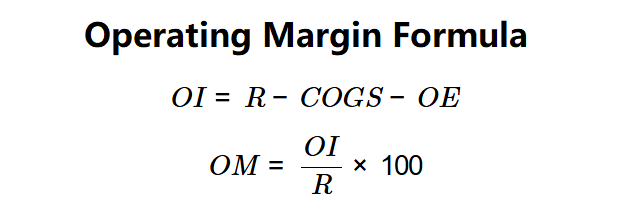
Definition: This calculator computes the operating margin (\( OM \)), which measures the percentage of revenue remaining after covering cost of goods sold and operating expenses, reflecting operational efficiency.
Purpose: Helps businesses and investors assess a company's core profitability before interest and taxes, aiding in performance evaluation and cost management.
The calculator follows a two-step process to compute \( OM \):
Formulas:
Steps:
Calculating \( OM \) is crucial for:
Example 1 (Company Alpha): \( R = \$10,000,000 \), \( COGS = \$5,000,000 \), \( OE = \$2,500,000 \):
An operating margin of 25.00% indicates strong operational profitability for Company Alpha.
Example 2: \( R = \$8,000,000 \), \( COGS = \$4,500,000 \), \( OE = \$2,000,000 \):
An operating margin of 18.75% suggests moderate operational efficiency.
Example 3: \( R = \$6,000,000 \), \( COGS = \$3,500,000 \), \( OE = \$3,000,000 \):
A negative operating margin of -8.33% indicates operational losses due to high expenses.
Q: What is operating margin?
A: Operating margin (\( OM \)) is the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting COGS and operating expenses, reflecting operational profitability.
Q: Why might OM be negative?
A: A negative \( OM \) occurs when operating expenses and COGS exceed revenue, indicating operational inefficiency.
Q: How does OM differ from net profit margin?
A: \( OM \) excludes interest and taxes, focusing on core operations, while net profit margin includes all expenses and taxes.