 Home
Home
 Back
Back
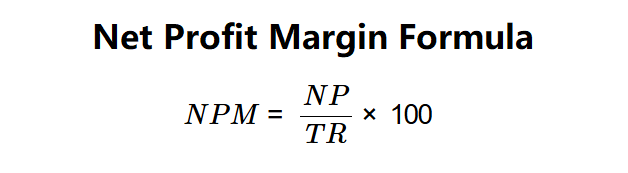
Definition: This calculator computes the net profit margin (\( NPM \)), which measures the percentage of total revenues that remains as net profit after all expenses.
Purpose: Helps businesses and investors evaluate profitability efficiency, compare performance across companies, and assess financial health.
The calculator follows a single-step process to compute \( NPM \):
Formula:
Steps:
Note: The result is displayed as a percentage; it can also be expressed as a decimal (e.g., 13% = 0.13) for certain analyses, though the calculator defaults to percentage.
Calculating \( NPM \) is crucial for:
Example 1: \( NP = \$24,500 \), \( TR = \$100,000 \):
A net profit margin of 24.50% indicates strong profitability per revenue dollar.
Example 2: \( NP = \$5,000 \), \( TR = \$50,000 \):
A net profit margin of 10.00% suggests moderate profitability.
Example 3: \( NP = \$-2,000 \), \( TR = \$20,000 \):
A negative net profit margin of -10.00% indicates a loss relative to revenue.
Q: What is net profit margin?
A: Net profit margin (\( NPM \)) is the percentage of total revenue that remains as net profit after all expenses.
Q: Why might NPM be negative?
A: A negative \( NPM \) occurs when expenses exceed revenues, resulting in a net loss.
Q: Can NPM be expressed as a decimal?
A: Yes, \( NPM \) can be expressed as a decimal (e.g., 13% = 0.13), though this calculator displays it as a percentage.