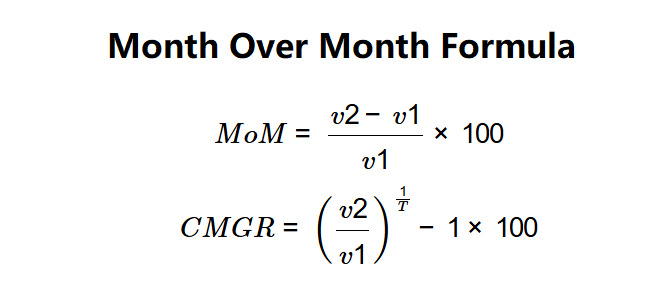1. What is the Month-over-Month and CMGR Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the month-over-month change (\( MoM \)) and compounding monthly growth rate (\( CMGR \)), which measure the percentage change between two months and the average monthly growth rate over a period, respectively.
Purpose: Helps businesses and analysts track growth trends, assess performance, and forecast future values based on historical data.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator follows a two-step process to compute \( MoM \) and \( CMGR \):
Formulas:
$$ MoM = \frac{v2 - v1}{v1} \times 100 $$
$$ CMGR = \left(\frac{v2}{v1}\right)^{\frac{1}{T}} - 1 \times 100 $$
Where:
- \( MoM \): Month-over-Month Change (percentage)
- \( CMGR \): Compounding Monthly Growth Rate (percentage)
- \( v1 \): Value in Month 1 (units)
- \( v2 \): Value in Month 2 (units)
- \( T \): Period Duration in Months
Steps:
- Step 1: Determine \( v1 \) and \( v2 \). Input the values for month 1 and month 2.
- Step 2: Determine \( T \). Input the period duration in months between the two values.
- Step 3: Calculate \( MoM \). Compute the percentage change from \( v1 \) to \( v2 \).
- Step 4: Calculate \( CMGR \). Compute the average monthly growth rate over the period using the compound formula.
3. Importance of MoM and CMGR Calculation
Calculating \( MoM \) and \( CMGR \) is crucial for:
- Trend Analysis: \( MoM \) provides a quick snapshot of monthly performance changes.
- Growth Forecasting: \( CMGR \) offers a compounded average growth rate, useful for long-term planning.
- Performance Monitoring: Helps identify consistent growth or decline over time.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Social Media Followers):
\( v1 = 100 \), \( v2 = 200 \), \( T = 5 \) months:
- Step 1: \( v1 = 100 \), \( v2 = 200 \).
- Step 2: \( T = 5 \) months.
- Step 3: \( MoM = \frac{200 - 100}{100} \times 100 = 100.00\% \).
- Step 4: \( CMGR = \left(\frac{200}{100}\right)^{\frac{1}{5}} - 1 \times 100 \approx 14.87\% \).
- Results: \( MoM = 100.00\% \), \( CMGR = 14.87\% \).
A \( MoM \) of 100.00% and \( CMGR \) of 14.87% indicate strong growth from January to June.
Example 2:
\( v1 = 500 \), \( v2 = 550 \), \( T = 3 \) months:
- Step 1: \( v1 = 500 \), \( v2 = 550 \).
- Step 2: \( T = 3 \) months.
- Step 3: \( MoM = \frac{550 - 500}{500} \times 100 = 10.00\% \).
- Step 4: \( CMGR = \left(\frac{550}{500}\right)^{\frac{1}{3}} - 1 \times 100 \approx 3.17\% \).
- Results: \( MoM = 10.00\% \), \( CMGR = 3.17\% \).
A \( MoM \) of 10.00% and \( CMGR \) of 3.17% suggest moderate growth over three months.
Example 3:
\( v1 = 1,000 \), \( v2 = 900 \), \( T = 2 \) months:
- Step 1: \( v1 = 1,000 \), \( v2 = 900 \).
- Step 2: \( T = 2 \) months.
- Step 3: \( MoM = \frac{900 - 1,000}{1,000} \times 100 = -10.00\% \).
- Step 4: \( CMGR = \left(\frac{900}{1,000}\right)^{\frac{1}{2}} - 1 \times 100 \approx -5.12\% \).
- Results: \( MoM = -10.00\% \), \( CMGR = -5.12\% \).
A \( MoM \) of -10.00% and \( CMGR \) of -5.12% indicate a decline in value over two months.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is month-over-month change?
A: Month-over-month change (\( MoM \)) is the percentage increase or decrease in value from month 1 to month 2.
Q: What does CMGR represent?
A: Compounding monthly growth rate (\( CMGR \)) is the average monthly growth rate compounded over a period.
Q: Can MoM be negative?
A: Yes, a negative \( MoM \) indicates a decrease in value between the two months.
Month-over-Month and CMGR Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2026
 Home
Home
 Back
Back