 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the marginal revenue (\( MR \)), which represents the additional revenue generated by selling one more unit of a good or service.
Purpose: Helps businesses assess the revenue impact of increasing production or sales, aiding in pricing strategies and profit maximization.
The calculator follows a single-step process to compute \( MR \):
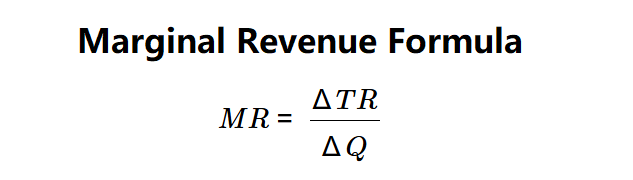
Formula:
Steps:
Note: A negative \( MR \) indicates a decrease in revenue per additional unit, suggesting a need to review pricing or demand strategies.
Calculating \( MR \) is crucial for:
Example 1 (Magic 8 Balls): \( TR1 = \$50,000 \), \( Q1 = 1,000 \), \( TR2 = \$62,000 \), \( Q2 = 1,200 \):
A marginal revenue of $60 per unit indicates a positive revenue increase for the additional 200 units.
Example 2: \( TR1 = \$10,000 \), \( Q1 = 500 \), \( TR2 = \$11,500 \), \( Q2 = 600 \):
A marginal revenue of $15 per unit suggests a moderate revenue gain per additional unit.
Example 3: \( TR1 = \$5,000 \), \( Q1 = 300 \), \( TR2 = \$4,800 \), \( Q2 = 350 \):
A negative marginal revenue of -$4 per unit indicates a revenue decrease, suggesting a need to adjust strategy.
Q: What is marginal revenue?
A: Marginal revenue (\( MR \)) is the additional revenue from selling one more unit of a good or service.
Q: What does a negative MR mean?
A: A negative \( MR \) indicates that selling additional units reduces total revenue, possibly due to price decreases or demand issues.
Q: Can MR be used with marginal cost?
A: Yes, profit maximization occurs where \( MR = MC \) (marginal cost), a key principle in economic theory.