 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the Loan to Value ratio (V), the percentage of a property’s purchase price financed by a loan, used to assess lending risk.
Purpose: Helps borrowers and lenders evaluate mortgage eligibility, interest rates, and insurance requirements, as higher LTV ratios indicate higher risk.
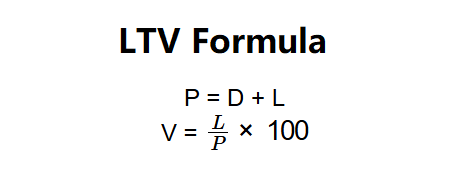
The calculator uses these formulas:
Formulas:
Steps:
Calculating LTV is key for:
Example: For a property with \( L = \$400,000 \), \( D = \$100,000 \):
This shows the loan covers 80% of the property’s value, a common threshold for favorable mortgage terms.
Q: How do I calculate the loan to value ratio?
A: LTV is calculated in three steps: (1) Input the loan amount (\( L \)) and either the purchase price (\( P \)) or down payment (\( D \)); (2) Calculate the purchase price if needed using \( P = D + L \); (3) Calculate LTV using \( V = \frac{L}{P} \times 100 \). For example, a $400,000 loan with a $100,000 down payment yields \( P = 500,000 \), \( V = \frac{400,000}{500,000} \times 100 = 80\% \).
Q: What is a good LTV ratio?
A: An LTV of 80% or lower is typically preferred, as it often avoids private mortgage insurance (PMI) and secures better loan terms. Higher LTVs increase lender risk.
Q: How does LTV affect my mortgage?
A: Higher LTVs may lead to higher interest rates, additional insurance requirements, or loan denial, as they indicate greater risk for lenders.