1. What is the Lease Calculator?
Definition: The Lease Calculator estimates the down payment, residual value, monthly payment, total payments, total interest, and total cost to own for a leasing contract, based on product value, lease amount, residual value, interest rate, and lease term.
Purpose: This tool helps users evaluate the financial implications of leasing an asset (e.g., a car or equipment), aiding in decisions about leasing versus buying by comparing total costs and monthly obligations.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
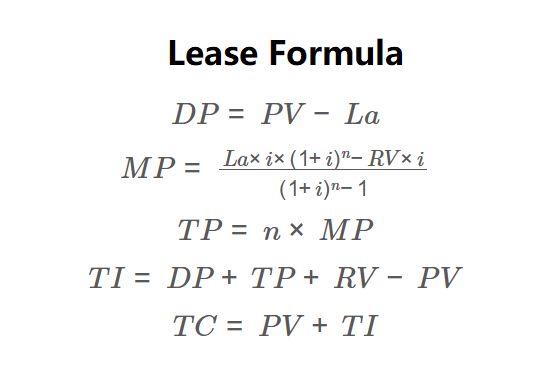
\( DP = PV - La \)
\( MP = \frac{La \times i \times (1 + i)^n - RV \times i}{(1 + i)^n - 1} \)
\( TP = n \times MP \)
\( TI = DP + TP + RV - PV \)
\( TC = PV + TI \)
Where:
- \( DP \): Down payment ($);
- \( PV \): Product value ($);
- \( La \): Lease amount ($);
- \( RV \): Residual value ($);
- \( i \): Monthly interest rate (decimal, annual rate / 12);
- \( n \): Lease term (months);
- \( MP \): Monthly payment ($);
- \( TP \): Total payments ($);
- \( TI \): Total interest ($);
- \( TC \): Total cost to own ($).
Steps:
- Enter product value, lease amount, residual value, annual interest rate, and lease term (months).
- Calculate down payment: \( DP = PV - La \).
- Calculate monthly interest rate: \( i = \frac{\text{annual rate}}{12} \).
- Calculate monthly payment using the lease formula.
- Calculate total payments: \( TP = n \times MP \).
- Calculate total interest: \( TI = DP + TP + RV - PV \).
- Calculate total cost to own: \( TC = PV + TI \).
- Display results in currency format.
3. Importance of Lease Calculation
Calculating lease payments is essential for:
- Financial Planning: Determines monthly and total costs, helping assess affordability compared to buying.
- Cost Comparison: Evaluates total interest and cost to own, aiding decisions between leasing and purchasing via loans.
- Budget Management: Ensures lease payments fit within monthly budgets, considering lease amount and residual value impacts.
4. Using the Calculator
Example: Calculate the lease payments for an asset worth $30,000 with a $25,000 lease amount, $14,000 residual value, 4% interest rate, and 48-month lease term:
- Product Value (\( PV \)): $30,000; Lease Amount (\( La \)): $25,000;
- Down Payment (\( DP \)): \( 30000 - 25000 = 5000 \);
- Residual Value (\( RV \)): $14,000;
- Interest Rate: 4% (\( i = 0.04 / 12 \approx 0.003333 \)); Lease Term (\( n \)): 48;
- Monthly Payment (\( MP \)): \( \frac{25000 \times 0.003333 \times (1.003333)^{48} - 14000 \times 0.003333}{(1.003333)^{48} - 1} \approx 295.04 \);
- Total Payments (\( TP \)): \( 48 \times 295.04 \approx 14161.74 \);
- Total Interest (\( TI \)): \( 5000 + 14161.74 + 14000 - 30000 = 3161.74 \);
- Total Cost to Own (\( TC \)): \( 30000 + 3161.74 = 33161.74 \);
- Result: Down Payment: $5,000.00; Residual Value: $14,000.00; Monthly Payment: $295.04; Total Payments: $14,161.74; Total Interest: $3,161.74; Total Cost to Own: $33,161.74.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a lease?
A: A lease is a contract allowing use of an asset (e.g., a car or equipment) for a fixed period in exchange for periodic payments, with an option to purchase at the residual value.
Q: How does residual value affect lease payments?
A: A higher residual value reduces monthly payments, as it lowers the amount financed over the lease term, but increases the cost to own if purchasing the asset.
Q: Should I lease or buy?
A: Compare the total cost to own from leasing with the cost of buying. Leasing may offer lower monthly payments but higher long-term costs due to interest and residual value.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back