 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes labor productivity, measuring output (revenue) per employee or per hour, and can solve for missing values (revenue, employees, or hours) when two are provided.
Purpose: Helps businesses assess workforce efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and forecast production capacity.
The calculator supports two productivity metrics and reverse calculation:
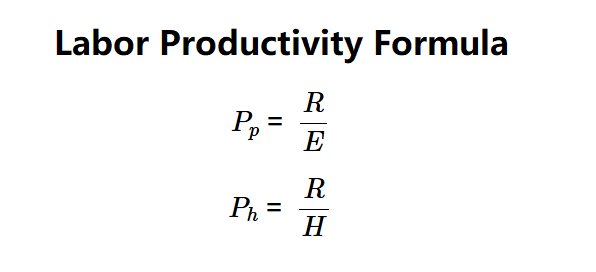
Formulas:
Steps:
Note: If both \( E \) and \( H \) are provided, productivity is calculated for both metrics. Reverse calculation assumes a default productivity rate when multiple values are missing.
Calculating labor productivity is crucial for:
Example 1 (House Cleaning): \( R = \$1,200 \), \( E = 2 \), \( H = 8 \):
Productivity of $600 per person and $150 per hour reflects efficient cleaning output.
Example 2 (Solve for Employees): \( R = \$12,300 \), \( H = 160 \) (40 hours/week × 4 weeks), \( P_p = \$77 \) (assumed from Mark's example):
Approximately 160 employees match Mark’s productivity if hours are consistent.
Example 3 (Solve for Revenue): \( E = 2 \), \( H = 96 \) (24 hours/week × 4 weeks), \( P_h = \$57 \) (from Rob’s example):
A revenue of $5,472 aligns with Rob’s productivity per hour.
Q: What is labor productivity?
A: Labor productivity measures output (revenue) per employee or per hour, indicating work efficiency.
Q: Can productivity be calculated per machine?
A: Yes, the formula applies to machines by substituting the number of machines for employees or hours.
Q: What if revenue is zero?
A: Zero revenue is invalid as it leads to undefined productivity; inputs must be positive.