 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: Future Value (FV) is the value of a current asset or investment at a specified date in the future, based on an assumed rate of growth or interest.
Purpose: Calculating the future value helps investors and financial planners understand how much an investment made today will be worth in the future, aiding in decision-making for savings, investments, and financial goals.
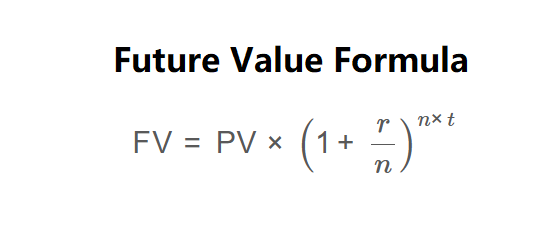
The calculator uses the following formula for Future Value, as shown in the image above:
\[ \text{FV} = \text{PV} \times \left(1 + \frac{r}{n}\right)^{n \times t} \]
Where:
Steps:
Calculating Future Value is essential for:
Example 1: Calculate the future value of a single investment
Example 2: Calculate the future value with monthly compounding
Q: Why does the compounding frequency matter?
A: More frequent compounding (e.g., monthly vs. annually) results in a higher future value because interest is calculated on the accumulated interest more often.
Q: How does the time value of money affect future value?
A: The time value of money principle states that money today is worth more than the same amount in the future because it can earn interest, which is why future value calculations account for growth over time.
Q: Can future value be negative?
A: No, future value cannot be negative as long as the present value and interest rate are non-negative, since the formula involves multiplication and exponentiation of positive values.
Q: What if my investment doesn’t compound interest?
A: If interest is not compounded (simple interest), you can set the compounding frequency to 1 and adjust the time period to 1 year to calculate the future value using simple interest: \( \text{FV} = \text{PV} \times (1 + r \times t) \).