 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: A Fixed Deposit (FD) is a financial instrument offered by banks and financial institutions where you deposit a lump sum for a fixed period at a predetermined interest rate, earning guaranteed returns.
Purpose: FDs provide a safe, low-risk investment option with assured returns, ideal for financial planning, such as saving for future goals or earning steady interest income.
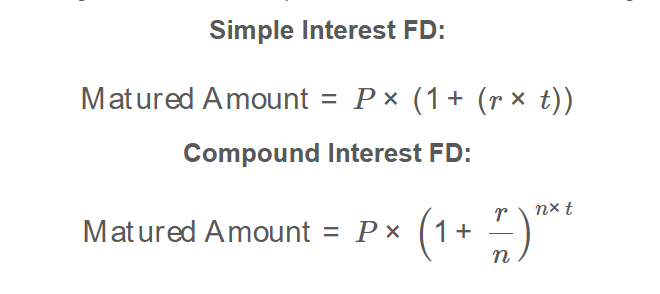
The calculator uses the following formulas for Fixed Deposit calculations, as shown in the image above:
Simple Interest FD: \[ \text{Matured Amount} = P \times (1 + (r \times t)) \]
Compound Interest FD: \[ \text{Matured Amount} = P \times \left(1 + \frac{r}{n}\right)^{n \times t} \]
Where:
Steps:
Calculating FD returns is essential for:
Example 1: Calculate the maturity amount for a simple interest FD
Example 2: Calculate the maturity amount for a compound interest FD
Q: What is the difference between simple and compound interest FDs?
A: Simple interest FDs calculate interest only on the principal, while compound interest FDs calculate interest on the principal plus accumulated interest, leading to higher returns over time.
Q: Can I withdraw my FD before maturity?
A: Yes, but you may incur a penalty or lose some accrued interest, depending on the bank’s policy.
Q: Are FD returns taxable?
A: Yes, interest earned on FDs is typically taxable as income, subject to your local tax laws.
Q: Why does compounding frequency matter?
A: More frequent compounding (e.g., monthly vs. annually) results in higher returns because interest is calculated on the growing balance more often.