 Home
Home
 Back
Back
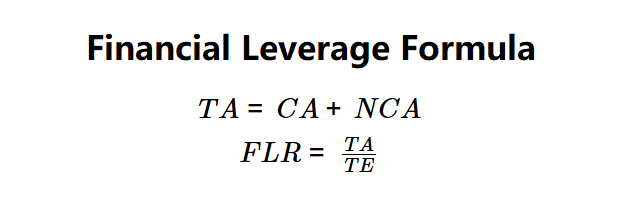
Definition: This calculator computes the financial leverage ratio (\( FLR \)), which measures the proportion of a company's total assets financed by debt relative to equity, indicating the degree of financial leverage.
Purpose: Helps investors, creditors, and businesses assess the risk associated with debt financing and the company's ability to meet obligations.
The calculator follows a three-step process to compute the financial leverage ratio:
Formulas:
Steps:
Calculating the financial leverage ratio is crucial for:
Example 1 (Company Alpha): \( CA = \$500,000 \), \( NCA = \$3,000,000 \), \( TE = \$1,500,000 \):
A financial leverage ratio of 2.33x indicates that total assets are 2.33 times equity, suggesting moderate leverage.
Example 2: \( CA = \$200,000 \), \( NCA = \$800,000 \), \( TE = \$400,000 \):
A financial leverage ratio of 2.50x shows a slightly higher reliance on debt.
Example 3: \( CA = \$1,000,000 \), \( NCA = \$2,000,000 \), \( TE = \$3,000,000 \):
A financial leverage ratio of 1.00x indicates no debt financing, relying solely on equity.
Q: What is the financial leverage ratio?
A: The financial leverage ratio (\( FLR \)) measures the extent to which a company uses debt to finance its assets relative to equity.
Q: What does a high financial leverage ratio mean?
A: A high \( FLR \) suggests greater use of debt, increasing financial risk but potentially enhancing returns on equity.
Q: Can the financial leverage ratio be less than 1?
A: Yes, if total assets are less than total equity (e.g., due to revaluation or specific accounting treatments), though this is rare.