1. What is the Earnings Before Tax Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the earnings before tax (\( EBT \)), which represents a company's profit after operating expenses and interest but before income taxes, providing a key measure of operational performance.
Purpose: Helps businesses, investors, and analysts evaluate profitability before tax obligations, aiding in financial planning and performance comparison.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator follows a four-step process to compute EBT:
Formulas:
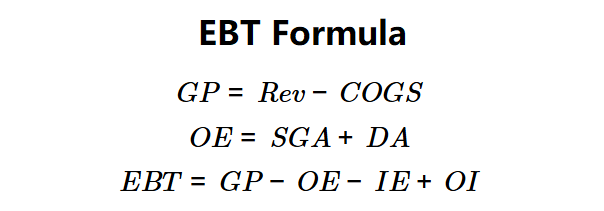
\( GP = Rev - COGS \)
\( OE = SGA + DA \)
\( EBT = GP - OE - IE + OI \)
Where:
- \( EBT \): Earnings Before Tax (dollars)
- \( GP \): Gross Profit (dollars)
- \( OE \): Operating Expenses (dollars)
- \( Rev \): Revenue (dollars)
- \( COGS \): Cost of Goods Sold (dollars)
- \( SGA \): Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses (dollars)
- \( DA \): Depreciation and Amortization (dollars)
- \( IE \): Interest Expense (dollars)
- \( OI \): Other Income (dollars)
Steps:
- Step 1: Compute \( GP \). Subtract \( COGS \) from \( Rev \).
- Step 2: Compute \( OE \). Add \( SGA \) and \( DA \).
- Step 3: Determine \( IE \). Input the interest expense.
- Step 4: Determine \( OI \). Input other income.
- Step 5: Calculate \( EBT \). Subtract \( OE \) and \( IE \) from \( GP \), then add \( OI \).
3. Importance of Earnings Before Tax Calculation
Calculating EBT is crucial for:
- Profitability Analysis: Provides a pre-tax view of operational success.
- Tax Planning: Helps estimate tax liabilities and optimize tax strategies.
- Investment Decisions: Assists investors in comparing company performance across tax jurisdictions.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Company Alpha):
\( Rev = \$1,000,000 \), \( COGS = \$300,000 \), \( SGA = \$150,000 \), \( DA = \$150,000 \), \( IE = \$200,000 \), \( OI = \$100,000 \):
- Step 1: \( GP = 1,000,000 - 300,000 = \$700,000 \).
- Step 2: \( OE = 150,000 + 150,000 = \$300,000 \).
- Step 3: \( IE = \$200,000 \).
- Step 4: \( OI = \$100,000 \).
- Step 5: \( EBT = 700,000 - 300,000 - 200,000 + 100,000 = \$300,000 \).
- Results: \( GP = \$700,000 \), \( OE = \$300,000 \), \( EBT = \$300,000 \).
An EBT of $300,000 reflects Company Alpha's pre-tax profit.
Example 2:
\( Rev = \$2,000,000 \), \( COGS = \$800,000 \), \( SGA = \$300,000 \), \( DA = \$200,000 \), \( IE = \$150,000 \), \( OI = \$50,000 \):
- Step 1: \( GP = 2,000,000 - 800,000 = \$1,200,000 \).
- Step 2: \( OE = 300,000 + 200,000 = \$500,000 \).
- Step 3: \( IE = \$150,000 \).
- Step 4: \( OI = \$50,000 \).
- Step 5: \( EBT = 1,200,000 - 500,000 - 150,000 + 50,000 = \$600,000 \).
- Results: \( GP = \$1,200,000 \), \( OE = \$500,000 \), \( EBT = \$600,000 \).
An EBT of $600,000 indicates strong pre-tax earnings.
Example 3:
\( Rev = \$500,000 \), \( COGS = \$400,000 \), \( SGA = \$50,000 \), \( DA = \$30,000 \), \( IE = \$100,000 \), \( OI = \$20,000 \):
- Step 1: \( GP = 500,000 - 400,000 = \$100,000 \).
- Step 2: \( OE = 50,000 + 30,000 = \$80,000 \).
- Step 3: \( IE = \$100,000 \).
- Step 4: \( OI = \$20,000 \).
- Step 5: \( EBT = 100,000 - 80,000 - 100,000 + 20,000 = \$-40,000 \).
- Results: \( GP = \$100,000 \), \( OE = \$80,000 \), \( EBT = \$-40,000 \).
An EBT of -$40,000 indicates a pre-tax loss.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is earnings before tax?
A: Earnings before tax (\( EBT \)) is the profit a company earns before accounting for income taxes, calculated from gross profit, operating expenses, interest, and other income.
Q: Why is EBT important?
A: It provides a clear view of operational profitability before tax impacts, useful for cross-company comparisons and tax planning.
Q: Can EBT be negative?
A: Yes, if operating expenses and interest exceed gross profit plus other income, \( EBT \) can be negative, indicating a loss.
Earnings Before Tax Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back