 Home
Home
 Back
Back
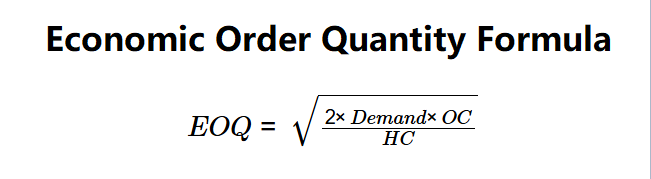
Definition: This calculator computes the economic order quantity (\( EOQ \)), which determines the optimal order quantity that minimizes the total inventory costs (ordering and holding costs) for a given demand.
Purpose: Helps businesses optimize inventory management, reduce costs, and improve cash flow by determining the ideal order size.
The calculator uses the following formula to compute EOQ:
Formula:
Steps:
Assumptions: Ordering and holding costs, as well as demand, remain constant throughout the year.
Calculating EOQ is crucial for:
Example 1 (Notepads): \( Demand = 500,000 \), \( OC = \$10 \), \( HC = \$4 \):
An EOQ of 1,581.14 units optimizes inventory costs for notepads.
Example 2: \( Demand = 1,000,000 \), \( OC = \$15 \), \( HC = \$5 \):
An EOQ of 2,449.49 units suggests a larger optimal order for higher demand.
Example 3: \( Demand = 250,000 \), \( OC = \$8 \), \( HC = \$2 \):
An EOQ of 1,414.21 units indicates a moderate order size for lower demand.
Q: What is economic order quantity?
A: Economic order quantity (\( EOQ \)) is the optimal number of units to order that minimizes total inventory costs, balancing ordering and holding costs.
Q: What happens if holding costs increase?
A: An increase in holding costs reduces the \( EOQ \), leading to smaller, more frequent orders.
Q: Can EOQ be zero?
A: No, since demand, order cost, and holding cost are positive, \( EOQ \) will always be positive.